NMP-7 inhibits chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain via block of Cav3.2 T-type calcium channels and activation of CB2 receptors
- PMID: 25481027
- PMCID: PMC4271433
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-8069-10-77
NMP-7 inhibits chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain via block of Cav3.2 T-type calcium channels and activation of CB2 receptors
Abstract
Background: T-type calcium channels and cannabinoid receptors are known to play important roles in chronic pain, making them attractive therapeutic targets. We recently reported on the design, synthesis and analgesic properties of a novel T-type channel inhibitor (NMP-7), which also shows mixed agonist activity on CB1 and CB2 receptors in vitro. Here, we analyzed the analgesic effect of systemically delivered NMP-7 (intraperitoneal (i.p.) or intragstric (i.g.) routes) on mechanical hypersensitivity in inflammatory pain induced by Complete Freund's Adjuvant (CFA) and neuropathic pain induced by sciatic nerve injury.
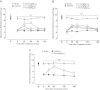
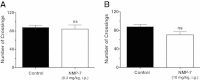
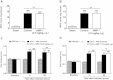
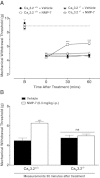
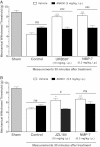
Results: NMP-7 delivered by either i.p. or i.g. routes produced dose-dependent inhibition of mechanical hyperalgesia in mouse models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain, without altering spontaneous locomotor activity in the open-field test at the highest active dose. Neither i.p. nor i.g. treatment reduced peripheral inflammation per se, as evaluated by examining paw edema and myeloperoxidase activity. The antinociception produced by NMP-7 in the CFA test was completely abolished in CaV3.2-null mice, confirming CaV3.2 as a key target. The analgesic action of intraperitoneally delivered NMP-7 was not affected by pretreatment of mice with the CB1 antagonist AM281, but was significantly attenuated by pretreatment with the CB2 antagonist AM630, suggesting that CB2 receptors, but not CB1 receptors are involved in the action of NMP-7 in vivo.
Conclusions: Overall, our work shows that NMP-7 mediates a significant analgesic effect in a model of persistent inflammatory and chronic neuropathic pain by way of T-type channel modulation and CB2 receptor activation. Thus, this study provides a novel therapeutic avenue for managing chronic pain conditions via mixed CB ligands/T-type channel blockers.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analgesic effect of a mixed T-type channel inhibitor/CB2 receptor agonist.Mol Pain. 2013 Jul 1;9:32. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-9-32. Mol Pain. 2013. PMID: 23815854 Free PMC article.
-
A cell-permeant peptide corresponding to the cUBP domain of USP5 reverses inflammatory and neuropathic pain.Mol Pain. 2016 Apr 29;12:1744806916642444. doi: 10.1177/1744806916642444. Print 2016. Mol Pain. 2016. PMID: 27130589 Free PMC article.
-
A role for cannabinoid receptors, but not endogenous opioids, in the antinociceptive activity of the CB2-selective agonist, GW405833.Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 Dec 28;528(1-3):65-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.10.043. Epub 2005 Nov 28. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16316650
-
[The cannabinoid system and pain: towards new drugs?].J Soc Biol. 2009;203(1):99-106. doi: 10.1051/jbio:2009002. Epub 2009 Apr 10. J Soc Biol. 2009. PMID: 19358815 Review. French.
-
Cannabinoid type 2 receptor as a target for chronic - pain.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2009 Jan;9(1):11-25. doi: 10.2174/138955709787001785. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19149657 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Ameliorates DSS-Induced Colitis through Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome in Macrophages.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 9;11(9):e0155076. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155076. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27611972 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclovirobuxine D, a cardiovascular drug from traditional Chinese medicine, alleviates inflammatory and neuropathic pain mainly via inhibition of voltage-gated Cav3.2 channels.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 21;13:1081697. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1081697. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36618940 Free PMC article.
-
Ion Channels Involved in Substance P-Mediated Nociception and Antinociception.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 30;20(7):1596. doi: 10.3390/ijms20071596. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30935032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Drug Development Overview: Targeting Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels for the Treatment of Pain.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 25;24(11):9223. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119223. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The terpenes camphene and alpha-bisabolol inhibit inflammatory and neuropathic pain via Cav3.2 T-type calcium channels.Mol Brain. 2021 Nov 14;14(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s13041-021-00876-6. Mol Brain. 2021. PMID: 34775970 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hildebrand ME, Snutch TP. Contributions of T-type calcium channels to the pathophysiology of pain signaling. Drug Discov Today Dis Mech. 2006;3:335–341. doi: 10.1016/j.ddmec.2006.10.001. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

