Serotonergic mechanism of the relieving effect of bee venom acupuncture on oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic cold allodynia in rats
- PMID: 25481535
- PMCID: PMC4295325
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-471
Serotonergic mechanism of the relieving effect of bee venom acupuncture on oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic cold allodynia in rats
Abstract
Background: Oxaliplatin, an important chemotherapy drug for advanced colorectal cancer, often induces peripheral neuropathy, especially cold allodynia. Our previous study showed that bee venom acupuncture (BVA), which has been traditionally used in Korea to treat various pain symptoms, potently relieves oxaliplatin-induced cold allodynia in rats. However, the mechanism for this anti-allodynic effect of BVA remains poorly understood. We investigated whether and how the central serotonergic system, a well-known pathway for acupuncture analgesia, mediates the relieving effect of BVA on cold allodynia in oxaliplatin-injected rats.
Methods: The behavioral signs of cold allodynia in Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were induced by a single injection of oxaliplatin (6 mg/kg, i.p.). Before and after BVA treatment, the cold allodynia signs were evaluated by immersing the rat's tail into cold water (4°C) and measuring the withdrawal latency. For BVA treatment, a diluted BV (0.25 mg/kg) was subcutaneously administered into Yaoyangguan (GV3) acupoint, which is located between the spinous processes of the fourth and the fifth lumbar vertebra. Serotonin was depleted by a daily injection of DL-p-chlorophenylalanine (PCPA, 150 mg/kg, i.p.) for 3 days. The amount of serotonin in the spinal cord was measured by ELISA. Serotonergic receptor antagonists were administered intraperitoneally or intrathecally before BVA treatment.
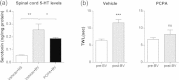
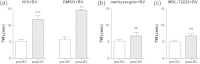
Results: The serotonin levels in the spinal cord were significantly increased by BVA treatment and such increase was significantly reduced by PCPA. This PCPA pretreatment abolished the relieving effect of BVA on oxaliplatin-induced cold allodynia. Either of methysergide (mixed 5-HT1/5-HT2 receptor antagonist, 1 mg/kg, i.p.) or MDL-72222 (5-HT3 receptor antagonist, 1 mg/kg, i.p) blocked the anti-allodynic effect of BVA. Further, an intrathecal injection of MDL-72222 (12 μg) completely blocked the BVA-induced anti-allodynic action, whereas NAN-190 (5-HT1A receptor antagonist, 15 μg, i.t.) or ketanserin (5-HT2A receptor antagonist, 30 μg, i.t.) did not.
Conclusions: These results suggest that BVA treatment alleviates oxaliplatin-induced acute cold allodynia in rats via activation of the serotonergic system, especially spinal 5-HT3 receptors. Thus, our findings may provide a clinically useful evidence for the application of BVA as an alternative therapeutic option for the management of peripheral neuropathy, a dose-limiting side effect that occurs after an administration of oxaliplatin.
Figures
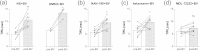
Similar articles
-
Involvement of Serotonergic System in Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathic Pain.Biomedicines. 2021 Aug 6;9(8):970. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9080970. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34440174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors Mediate the Suppressive Effect of an Injection of Diluted Bee Venom into the GV3 Acupoint on Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathic Cold Allodynia in Rats.Biol Pharm Bull. 2015;38(5):710-4. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b14-00797. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Biol Pharm Bull. 2015. PMID: 25752933
-
Combined Effects of Bee Venom Acupuncture and Morphine on Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Mice.Toxins (Basel). 2016 Jan 22;8(2):33. doi: 10.3390/toxins8020033. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 26805884 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of bee venom acupuncture on oxaliplatin-induced cold allodynia in rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:369324. doi: 10.1155/2013/369324. Epub 2013 Aug 22. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 24058370 Free PMC article.
-
Bee Venom Acupuncture Effects on Pain and Its Mechanisms: An Updated Review.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Aug 29;13(9):608. doi: 10.3390/toxins13090608. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34564611 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phytochemicals of Cinnamomi Cortex: Cinnamic Acid, but not Cinnamaldehyde, Attenuates Oxaliplatin-Induced Cold and Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats.Nutrients. 2019 Feb 19;11(2):432. doi: 10.3390/nu11020432. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30791474 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Serotonergic System in Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathic Pain.Biomedicines. 2021 Aug 6;9(8):970. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9080970. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34440174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acupuncture for Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Review of Clinical and Basic Studies.J Pain Res. 2021 Apr 15;14:993-1005. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S296150. eCollection 2021. J Pain Res. 2021. PMID: 33883931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noradrenergic inhibition of spinal hyperexcitation elicited by cutaneous cold stimuli in rats with oxaliplatin-induced allodynia: electrophysiological and behavioral assessments.J Physiol Sci. 2017 May;67(3):431-438. doi: 10.1007/s12576-016-0505-9. Epub 2016 Nov 28. J Physiol Sci. 2017. PMID: 27896597 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Lasting and Additive Analgesic Effects of Combined Treatment of Bee Venom Acupuncture and Venlafaxine on Paclitaxel-Induced Allodynia in Mice.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Sep 28;12(10):620. doi: 10.3390/toxins12100620. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32998357 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Argyriou AA, Briani C, Cavaletti G, Bruna J, Alberti P, Velasco R, Lonardi S, Cortinovis D, Cazzaniga M, Campagnolo M, Santos C, Kalofonos HP. Advanced age and liability to oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy: post hoc analysis of a prospective study. Eur J Neurol. 2013;20(5):788–794. doi: 10.1111/ene.12061. - DOI - PubMed
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6882/14/471/prepub
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

