K303⁶·⁵⁸ in the μ opioid (MOP) receptor is important in conferring selectivity for covalent binding of β-funaltrexamine (β-FNA)
- PMID: 25481857
- PMCID: PMC4314454
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.11.028
K303⁶·⁵⁸ in the μ opioid (MOP) receptor is important in conferring selectivity for covalent binding of β-funaltrexamine (β-FNA)
Abstract
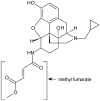
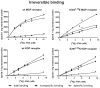
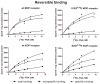
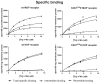
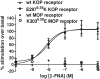
β-funaltrexamine (β-FNA) is an irreversible μ opioid (MOP) receptor antagonist and a reversible agonist of κ opioid (KOP) receptor. β-FNA binds covalently to the MOP receptor at Lys233(5.39), which is conserved among opioid receptors. Molecular docking of β-FNA showed that K303(6.58) in the MOP receptor and E297(6.58) in the KOP receptor played distinct roles in positioning β-FNA. K303(6.58)E MOP receptor and E297(6.58)K KOP receptor mutants were generated. The mutations did not affect β-FNA affinity or efficacy. K303(6.58)E mutation in the MOP receptor greatly reduced covalent binding of [(3)H]β-FNA; however, E297(6.58)K did not enable the KOP receptor to bind irreversibly to β-FNA. Molecular modeling demonstrated that the ε-amino group of K303(6.58) in the MOP receptor interacted with CO of the acetate group of β-FNA to facilitate covalent bond formation with Lys233(5.39). Replacement of K303(6.58) with Glu in the MOP receptor resulted in repulsion between the COOH of Glu and the CO of β-FNA and increased the distance between K233(5.39) and the fumarate group, making it impossible for covalent bond formation. These findings will be helpful for design of selective non-peptide MOP receptor antagonists.
Keywords: Irreversible binding; Kappa opioid receptor; Mu opioid receptor; β-funaltrexamine.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
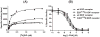
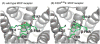
Similar articles
-
Methocinnamox is a potent, long-lasting, and selective antagonist of morphine-mediated antinociception in the mouse: comparison with clocinnamox, beta-funaltrexamine, and beta-chlornaltrexamine.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000 Sep;294(3):933-40. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000. PMID: 10945843
-
Determination of the amino acid residue involved in [3H]beta-funaltrexamine covalent binding in the cloned rat mu-opioid receptor.J Biol Chem. 1996 Aug 30;271(35):21422-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.35.21422. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8702924
-
Studies on kinetics of [3H]beta-funaltrexamine binding to mu opioid receptor.Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;37(2):243-50. Mol Pharmacol. 1990. PMID: 2154672
-
Endomorphin-induced motivational effect: differential mechanism of endomorphin-1 and endomorphin-2.Jpn J Pharmacol. 2002 Jul;89(3):224-8. doi: 10.1254/jjp.89.224. Jpn J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12184726 Review.
-
Incomplete cross tolerance and multiple mu opioid peptide receptors.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001 Feb;22(2):67-70. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(00)01616-3. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001. PMID: 11166849 Review.
Cited by
-
The opioid antagonist, β-funaltrexamine, inhibits NF-κB signaling and chemokine expression in human astrocytes and in mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Sep 5;762:193-201. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.05.040. Epub 2015 May 22. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26007645 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ballesteros JA, Weinstein H. Integrated methods for the construction of three dimensional models and computational probing of structure-function relations in G-protein coupled receptors. Methods Neurosci. 1995;25:366–428.
-
- Chen C, Xue JC, Zhu J, Chen YW, Kunapuli S, de Riel JK, Yu L, Liu-Chen L-Y. Characterization of irreversible binding of beta-funaltrexamine to the cloned rat mu opioid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:17866–17870. - PubMed
-
- Chen C, Yin J, Riel JK, DesJarlais RL, Raveglia LF, Zhu J, Liu-Chen L-Y. Determination of the amino acid residue involved in [3H]beta-funaltrexamine covalent binding in the cloned rat mu-opioid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:21422–21429. - PubMed
-
- Hjorth SA, Thirstrup K, Grandy DK, Schwartz TW. Analysis of selective binding epitopes for the kappa-opioid receptor antagonist nor-binaltorphimine. Mol Pharmacol. 1995;47:1089–1094. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

