A distal locus element mediates IFN-γ priming of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated TNF gene expression
- PMID: 25482561
- PMCID: PMC4268019
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.11.011
A distal locus element mediates IFN-γ priming of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated TNF gene expression
Abstract
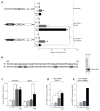
Interferon γ (IFN-γ) priming sensitizes monocytes and macrophages to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation, resulting in augmented expression of a set of genes including TNF. Here, we demonstrate that IFN-γ priming of LPS-stimulated TNF transcription requires a distal TNF/LT locus element 8 kb upstream of the TNF transcription start site (hHS-8). IFN-γ stimulation leads to increased DNase I accessibility of hHS-8 and its recruitment of interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF1), and subsequent LPS stimulation enhances H3K27 acetylation and induces enhancer RNA synthesis at hHS-8. Ablation of IRF1 or targeting the hHS-8 IRF1 binding site in vivo with Cas9 linked to the KRAB repressive domain abolishes IFN-γ priming, but does not affect LPS induction of the gene. Thus, IFN-γ poises a distal enhancer in the TNF/LT locus by chromatin remodeling and IRF1 recruitment, which then drives enhanced TNF gene expression in response to a secondary toll-like receptor (TLR) stimulus.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


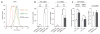
References
-
- Barthel R, Goldfeld AE. T cell-specific expression of the human TNF-alpha gene involves a functional and highly conserved chromatin signature in intron 3. J Immunol. 2003;171:3612–3619. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

