Two-pore domain potassium channels enable action potential generation in the absence of voltage-gated potassium channels
- PMID: 25482670
- PMCID: PMC4428809
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-014-1660-6
Two-pore domain potassium channels enable action potential generation in the absence of voltage-gated potassium channels
Abstract
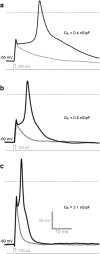
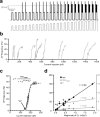
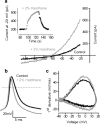
In this study, we explored the possibility that two-pore domain potassium (K2P) channels are sufficient to support action potential (AP) generation in the absence of conventional voltage-gated potassium (KV) channels. Hodgkin-Huxley parameters were used to mimic the presence of voltage-gated sodium (NaV) channels in HEK-293 cells. Recombinant expression of either TREK-1 or TASK-3 channels was then used to generate a hyperpolarised resting membrane potential (RMP) leading to the characteristic non-linear current-voltage relationship expected of a K2P-mediated conductance. During conductance simulation experiments, both TASK-3 and TREK-1 channels were able to repolarise the membrane once AP threshold was reached, and at physiologically relevant current densities, this K2P-mediated conductance supported sustained AP firing. Moreover, the magnitude of the conductance correlated with the speed of the AP rise in a manner predicted from our computational studies. We discuss the physiological impact of axonal K2P channels and speculate on the possible clinical relevance of K2P channel modulation when considering the actions of general and local anaesthetics.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The mammalian nodal action potential: new data bring new perspectives.Adv Physiol Educ. 2022 Dec 1;46(4):693-702. doi: 10.1152/advan.00171.2021. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Adv Physiol Educ. 2022. PMID: 36173340 Review.
-
Role of Voltage-Gated K+ Channels and K2P Channels in Intrinsic Electrophysiological Properties and Saltatory Conduction at Nodes of Ranvier of Rat Lumbar Spinal Ventral Nerves.J Neurosci. 2022 Jun 22;42(25):4980-4994. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0514-22.2022. Epub 2022 May 23. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35606142 Free PMC article.
-
TASK-3 two-pore domain potassium channels enable sustained high-frequency firing in cerebellar granule neurons.J Neurosci. 2007 Aug 29;27(35):9329-40. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1427-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17728447 Free PMC article.
-
PIP2 Mediated Inhibition of TREK Potassium Currents by Bradykinin in Mouse Sympathetic Neurons.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 8;21(2):389. doi: 10.3390/ijms21020389. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31936257 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Pharmacology of K2P Potassium Channels.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2021 Mar 6;55(S3):87-107. doi: 10.33594/000000339. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33667333 Review.
Cited by
-
Spike frequency-dependent inhibition and excitation of neural activity by high-frequency ultrasound.J Gen Physiol. 2020 Nov 2;152(11):e202012672. doi: 10.1085/jgp.202012672. J Gen Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33074301 Free PMC article.
-
Severe Convulsions and Dysmyelination in Both Jimpy and Cx32/47 -/- Mice may Associate Astrocytic L-Channel Function with Myelination and Oligodendrocytic Connexins with Internodal Kv Channels.Neurochem Res. 2017 Jun;42(6):1747-1766. doi: 10.1007/s11064-017-2194-z. Epub 2017 Feb 18. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 28214987 Review.
-
Effects of the two-pore potassium channel subunit Task5 on neuronal function and signal processing in the auditory brainstem.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Nov 1;18:1463816. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1463816. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39553828 Free PMC article.
-
K2P2.1 (TREK-1) potassium channel activation protects against hyperoxia-induced lung injury.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 15;10(1):22011. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78886-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33319831 Free PMC article.
-
Two-pore potassium channel TREK-1 (K2P2.1) regulates NLRP3 inflammasome activity in macrophages.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2024 Mar 1;326(3):L367-L376. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00313.2023. Epub 2024 Jan 22. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38252657 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aller MI, Veale EL, Linden AM, Sandu C, Schwaninger M, Evans LJ, Korpi ER, Mathie A, Wisden W, Brickley SG. Modifying the subunit composition of TASK channels alters the modulation of a leak conductance in cerebellar granule neurons. J Neurosci. 2005;25(49):11455–67. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3153-05.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alloui A, Zimmermann K, Mamet J, Duprat F, Noel J, Chemin J, Guy N, Blondeau N, Voilley N, Rubat-Coudert C, Borsotto M, Romey G, Heurteaux C, Reeh P, Eschalier A, Lazdunski M. TREK-1, a K+ channel involved in polymodal pain perception. EMBO J. 2006;25(11):2368–76. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601116. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

