Tenascin-C: Form versus function
- PMID: 25482829
- PMCID: PMC4422809
- DOI: 10.4161/19336918.2014.987587
Tenascin-C: Form versus function
Abstract
Tenascin-C is a large, multimodular, extracellular matrix glycoprotein that exhibits a very restricted pattern of expression but an enormously diverse range of functions. Here, we discuss the importance of deciphering the expression pattern of, and effects mediated by, different forms of this molecule in order to fully understand tenascin-C biology. We focus on both post transcriptional and post translational events such as splicing, glycosylation, assembly into a 3D matrix and proteolytic cleavage, highlighting how these modifications are key to defining tenascin-C function.
Keywords: AD1/AD2, additional domain 1/ additional domain 2; ADAMTS, a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs; ASMCs, aortic smooth muscle cells; BDNF, brain derived neurotrophic factor; BHKs, baby hamster kidney cells; BMP, bone morphogenetic protein; CA19–9, carbohydrate antigen 19–9; CALEB, chicken acidic leucine-rich EGF-like domain containing brain protein; CEA, carcinoembryonic antigen; CNS, central nervous system; CRC, colorectal carcinomas; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; DCIS, ductal carcinoma in-situ; ECM, extracellular matrix; EDA-FN, extra domain A containing fibronectin; EDB-FN, extra domain B containing fibronectin; EGF-L, epidermal growth factor-like; EGF-R, epidermal growth factor receptor; ELISPOT, enzyme-linked immunospot assay; FBG, fibrinogen-like globe; FGF2, fibroblast growth factor 2; FGF4, fibroblast growth factor 4; FN, fibronectin; FNIII, fibronectin type III-like repeat; GMEM, glioma-mesenchymal extracellular matrix antigen; GPI, glycosylphosphatidylinositol; HB-EGF, heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor; HCEs, immortalized human corneal epithelial cell line; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; HNK-1, human natural killer-1; HSPGs, heparan sulfate proteoglycans; HUVECs, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; ICC, immunocytochemistry; IF, immunofluorescence; IFNγ, interferon gamma; IGF, insulin-like growth factor; IGF-BP, insulin-like growth factor-binding protein; IHC, immunohistochemistry; IL, interleukin; ISH, in situ hybridization; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; MPNSTs, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors; Mr, molecular mass; NB, northern blot; NF-kB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NK, natural killer cells; NSCLC, non-small cell lung carcinoma; NSCs, neural stem cells; NT, neurotrophin; PAMPs, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; PDGF, platelet derived growth factor; PDGF-Rβ, platelet derived growth factor receptor β; PIGF, phosphatidylinositol-glycan biosynthesis class F protein; PLCγ, phospholipase-C gamma; PNS, peripheral nervous system; PTPRζ1, receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase zeta; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; RCC, renal cell carcinoma; RD, rhabdomyosarcoma; RGD, arginylglycylaspartic acid; RT-PCR, real-time polymerase chain reaction; SB, Southern blot; SCC, squamous cell carcinoma; SMCs, smooth muscle cells; SVZ, sub-ventricular zone; TA, tenascin assembly domain; TGFβ, transforming growth factor β; TIMP, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α; TSS, transcription start site; UBC, urothelial bladder cancer; UCC, urothelial cell carcinoma; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VSMCs, vascular smooth muscle cells; VZ, ventricular zone; WB, immunoblot/ western blot; bFGF, basic fibroblast growth factor; biosynthesis; c, charged; cancer; ccRCC, clear cell renal cell carcinoma; chRCC, chromophobe-primary renal cell carcinoma; development; glycosylation; mAb, monoclonal antibody; matrix assembly; mitogen-activated protein kinase, MAPK; pHo, extracellular pH; pRCC, papillary renal cell carcinoma; proteolytic cleavage; siRNA, small interfering RNA; splicing; tenascin-C; therapeutics; transcription.
Figures
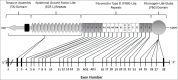

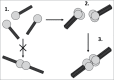
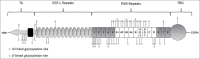
References
-
- Midwood KS, Orend G. The role of tenascin-C in tissue injury and tumorigenesis. J Cell Commun Signal 2009; 3:287-310; PMID:19838819; http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12079-009-0075-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chiquet-Ehrismann R, Orend G, Chiquet M, Tucker RP, Midwood KS. Tenascins in stem cell niches. Matrix Biol 2014; 37C:112-23; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2014.01.007 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Orend G, Saupe F, Schwenzer A, and Midwood, KS. The extracellular matrix and cancer: regulation of tumor cell biology by tenascin-C. iConcept Press 2014. ISBN: 978-1-922227-25-6.
-
- Forsberg E, Hirsch E, Frohlich L, Meyer M, Ekblom P, Aszodi A, Werner S, Fassler R. Skin wounds and severed nerves heal normally in mice lacking tenascin-C. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 1996; 93:6594-9; PMID:8692862; http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.13.6594 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fukamauchi F, Wang YJ, Mataga N, Kusakabe M. Effects of cholecystokinin-B receptor antagonist on dopamine system in tenascin mutant mice. Neuroreport 1997; 8:3919-22; PMID:9462466; http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00001756-199712220-00015 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
