Investigating the function of Fc-specific binding of IgM to Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein 1 mediating erythrocyte rosetting
- PMID: 25482886
- PMCID: PMC4737123
- DOI: 10.1111/cmi.12403
Investigating the function of Fc-specific binding of IgM to Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein 1 mediating erythrocyte rosetting
Abstract
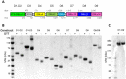
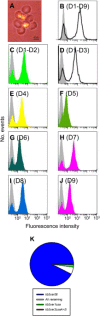
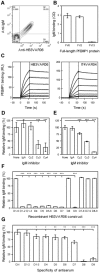
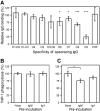
Acquired protection from Plasmodium falciparum malaria takes years to develop, probably reflecting the ability of the parasites to evade immunity. A recent example of this is the binding of the Fc region of IgM to VAR2CSA-type PfEMP1. This interferes with specific IgG recognition and phagocytosis of opsonized infected erythrocytes (IEs) without compromising the placental IE adhesion mediated by this PfEMP1 type. IgM also binds via Fc to several other PfEMP1 proteins, where it has been proposed to facilitate rosetting (binding of uninfected erythrocytes to a central IE). To further dissect the functional role of Fc -mediated IgM binding to PfEMP1, we studied the PfEMP1 protein HB3VAR06, which mediates rosetting and binds IgM. Binding of IgM to this PfEMP1 involved the Fc domains Cμ3-Cμ4 in IgM and the penultimate DBL domain (DBLζ2) at the C-terminus of HB3VAR06. However, IgM binding did not inhibit specific IgG labelling of HB3VAR06 or shield IgG-opsonized IEs from phagocytosis. Instead, IgM was required for rosetting, and each pentameric IgM molecule could bind two HB3VAR06 molecules. Together, our data indicate that the primary function of Fc -mediated IgM binding in rosetting is not to shield IE from specific IgG recognition and phagocytosis as in VAR2CSA-type PfEMP1. Rather, the function appears to be strengthening of IE-erythrocyte interactions. In conclusion, our study provides new evidence on the molecular details and functional significance of rosetting, a long-recognized marker of parasites that cause severe P. falciparum malaria.
© 2014 The Authors. Cellular Microbiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Barragan, A. , Spillmann, D. , Kremsner, P.G. , Wahlgren, M. , and Carlson, J. (1999) Plasmodium falciparum: molecular background to strain‐specific rosette disruption by glycosaminoglycans and sulfated glycoconjugates. Exp Parasitol 91: 133–143. - PubMed
-
- Barragan, A. , Fernandez, V. , Chen, Q. , von Euler, A. , Wahlgren, M. , and Spillmann, D. (2000a) The duffy‐binding‐like domain 1 of Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein 1 (PfEMP1) is a heparan sulfate ligand that requires 12 mers for binding. Blood 95: 3594–3599. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

