Dasatinib reverses the multidrug resistance of breast cancer MCF-7 cells to doxorubicin by downregulating P-gp expression via inhibiting the activation of ERK signaling pathway
- PMID: 25482933
- PMCID: PMC4622436
- DOI: 10.4161/15384047.2014.987062
Dasatinib reverses the multidrug resistance of breast cancer MCF-7 cells to doxorubicin by downregulating P-gp expression via inhibiting the activation of ERK signaling pathway
Abstract
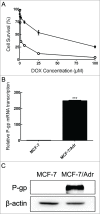
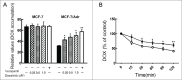
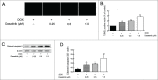
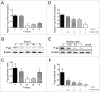
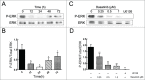
Multidrug resistance (MDR) is one of the major obstacles to the efficiency of cancer chemotherapy, which often results from the overexpression of drug efflux transporters such as P-glycoprotein (P-gp). In the present study, we determined the effect of dasatinib which was approved for imatinib resistant chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) and (Ph(+)) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) treatment on P-gp-mediated MDR. Our results showed that dasatinib significantly increased the sensitivity of P-gp-overexpressing MCF-7/Adr cells to doxorubicin in MTT assays; thus lead to an enhanced cytotoxicity of doxorubicin in MCF-7/Adr cells. Additionally, dasatinib increased the intracellular accumulation, inhibited the efflux of doxorubicin in MCF-7/Adr cells, and significantly enhanced doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in MCF-7/Adr cells. Further studies showed that dasatinib altered the expression levels of mRNA, protein levels of P-gp, and the phosphorylation of signal-regulated kinase (ERK) both in time-dependent (before 24 h) and dose-dependent manners at concentrations that produced MDR reversals. In conclusion, dasatinib reverses P-gp-mediated MDR by downregulating P-gp expression, which may be partly attributed to the inhibition of ERK pathway. Dasatinib may play an important role in circumventing MDR when combined with other conventional antineoplastic drugs.
Keywords: DOX, doxorubicin; ERK pathway; ERKextracellular signal-regulated kinase; MDR, multidrug resistance; P-ERK, phosphorylated extracellular signal–regulated kinase; P-glycoprotein; P-gp, P-glycoprotein; dasatinib; doxorubicin; multidrug resistance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting P-glycoprotein and SORCIN: Dihydromyricetin strengthens anti-proliferative efficiency of adriamycin via MAPK/ERK and Ca2+ -mediated apoptosis pathways in MCF-7/ADR and K562/ADR.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Apr;233(4):3066-3079. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26087. Epub 2017 Nov 14. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28681913
-
Survivin transcription is associated with P-glycoprotein/MDR1 overexpression in the multidrug resistance of MCF-7 breast cancer cells.Oncol Rep. 2010 May;23(5):1469-75. doi: 10.3892/or_00000786. Oncol Rep. 2010. PMID: 20372866
-
Reversal of multidrug resistance by gefitinib via RAF1/ERK pathway in pancreatic cancer cell line.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2012 Dec;295(12):2122-8. doi: 10.1002/ar.22552. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2012. PMID: 22907845
-
Improvement of conventional anti-cancer drugs as new tools against multidrug resistant tumors.Drug Resist Updat. 2020 May;50:100682. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2020.100682. Epub 2020 Feb 7. Drug Resist Updat. 2020. PMID: 32087558
-
Mapping the Role of P-gp in Multidrug Resistance: Insights from Recent Structural Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 28;26(9):4179. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094179. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362415 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial Peptide Reverses ABCB1-Mediated Chemotherapeutic Drug Resistance.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Aug 7;11:1208. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01208. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32903706 Free PMC article.
-
Sorcin: a novel potential target in therapies of cancers.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Aug 5;11:7327-7336. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S208677. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 31496794 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Autophagy and the Cytoprotective Role of Smac Mimetic against ROS-Induced Cancer: A Potential Therapeutic Strategy in Relapse and Chemoresistance Cases in Breast Cancer.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Jul 10;45(7):5752-5764. doi: 10.3390/cimb45070363. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37504279 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of AF-6/afadin induces cell invasion, suppresses the formation of glandular structures and might be a predictive marker of resistance to chemotherapy in endometrial cancer.BMC Cancer. 2015 Apr 12;15:275. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1286-x. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25879875 Free PMC article.
-
Ketone-selenoesters as potential anticancer and multidrug resistance modulation agents in 2D and 3D ovarian and breast cancer in vitro models.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 21;12(1):6548. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-10311-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35449387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Litman T, Druley TE, Stein WD, Bates SE. From MDR to MXR: new understanding of multidrug resistance systems, their properties and clinical significance. Cell Mol Life Sci 2001; 58: 931-59; PMID:11497241; http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/PL00000912 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Juliano RL, Ling V. A surface glycoprotein modulating drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Biochim Biophys Acta 1976; 455: 152-62; PMID:990323; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0005-2736(76)90160-7 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ambudkar SV, Kimchi-Sarfaty C, Sauna ZE, Gottesman MM. P-glycoprotein: from genomics to mechanism. Oncogene 2003; 22: 7468-85; PMID:14576852; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206948 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gottesman MM, Fojo T, Bates SE. Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 48-58; PMID:11902585; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrc706 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ghayad SE, Vendrell JA, Ben Larbi S, Dumontet C, Bieche I, Cohen PA. Endocrine resistance associated with activated ErbB system in breast cancer cells is reversed by inhibiting MAPK or PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Int J Cancer 2010; 126: 545-62; PMID:19609946; http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijc.24750 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
