USP7 controls Chk1 protein stability by direct deubiquitination
- PMID: 25483066
- PMCID: PMC4614819
- DOI: 10.4161/15384101.2014.973324
USP7 controls Chk1 protein stability by direct deubiquitination
Abstract
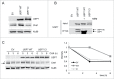
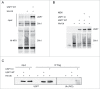
Chk1, an essential checkpoint kinase in the DNA damage response pathway (DDR), is tightly regulated by both ATR-dependent phosphorylation and proteasome-mediated degradation. Here we identify ubiquitin hydrolase USP7 as a novel regulator of Chk1 protein stability. USP7 was shown before to regulate other DDR proteins such as p53, Hdm2 and Claspin, an adaptor protein in the ATR-Chk1 pathway required for Chk1 activation. Depletion or inhibition of USP7 leads to lower Chk1 levels. The decreased Chk1 protein after USP7 knock down cannot be rescued by simultaneously elevating Claspin levels, demonstrating that the effect of USP7 on Chk1 is independent of its known effect on Claspin. Conversely, overexpression of USP7 wild type, but not a catalytic mutant version, elevates Chk1 levels and increases the half-life of Chk1 protein. Importantly, wild type, but not catalytic mutant USP7 can deubiquitinate Chk1 in vivo and in vitro, confirming that USP7 directly regulates Chk1 protein levels. Finally we show that USP7 catalytic mutant is (mono-)ubiquitinated, which suggests auto-deubiquitination by this ubiquitin hydrolase, possibly important for its regulation.
Keywords: CI, catalytic inactive; Chk1; DDR, DNA damage response; DUB, deubiquitylating enzyme; USP, ubiquitin specific peptidase; USP7; WT, wild type; claspin; ubiquitin hydrolase.
Figures

References
-
- Bartek J, Bartkova J, Lukas J. DNA damage signalling guards against activated oncogenes and tumour progression. Oncogene 2007; 26:7773-9; PMID:18066090; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210881 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Smits VAJ, Warmerdam DO, Martín Y, Freire R. Mechanisms of ATR-mediated checkpoint signalling. Front Biosci 2010; 15:840-53; http://dx.doi.org/10.2741/3649 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Smith J, Tho LM, Xu N, Gillespie DA. The ATM-Chk2 and ATR-Chk1 pathways in DNA damage signaling and cancer. Adv Cancer Res 2010; 108:73-112; PMID:21034966; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-380888-2.00003-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Smits VAJ, Reaper PM, Jackson SP. Rapid PIKK-dependent release of Chk1 from chromatin promotes the DNA-damage checkpoint response. Curr Biol 2006; 16:150-9; PMID:16360315; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2005.11.066 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Smits VAJ. Spreading the signal: dissociation of Chk1 from chromatin. Cell Cycle 2006; 5:1039-43; PMID:16721053; http://dx.doi.org/10.4161/cc.5.10.2761 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
