C/EBPα regulates CRL4(Cdt2)-mediated degradation of p21 in response to UVB-induced DNA damage to control the G1/S checkpoint
- PMID: 25483090
- PMCID: PMC4614632
- DOI: 10.4161/15384101.2014.962957
C/EBPα regulates CRL4(Cdt2)-mediated degradation of p21 in response to UVB-induced DNA damage to control the G1/S checkpoint
Abstract
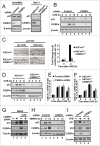
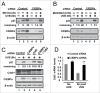
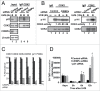
The bZIP transcription factor, C/EBPα is highly inducible by UVB and other DNA damaging agents in keratinocytes. C/EBPα-deficient keratinocytes fail to undergo cell cycle arrest in G1 in response to UVB-induced DNA damage and mice lacking epidermal C/EBPα are highly susceptible to UVB-induced skin cancer. The mechanism through which C/EBPα regulates the cell cycle checkpoint in response to DNA damage is unknown. Here we report untreated C/EBPα-deficient keratinocytes have normal levels of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, p21, however, UVB-treated C/EBPα-deficient keratinocytes fail to up-regulate nuclear p21 protein levels despite normal up-regulation of Cdkn1a mRNA levels. UVB-treated C/EBPα-deficient keratinocytes displayed a 4-fold decrease in nuclear p21 protein half-life due to the increased proteasomal degradation of p21 via the E3 ubiquitin ligase CRL4(Cdt2). Cdt2 is the substrate recognition subunit of CRL4(Cdt2) and Cdt2 mRNA and protein levels were up-regulated in UVB-treated C/EBPα-deficient keratinocytes. Knockdown of Cdt2 restored p21 protein levels in UVB-treated C/EBPα-deficient keratinocytes. Lastly, the failure to accumulate p21 in response to UVB in C/EBPα-deficient keratinocytes resulted in decreased p21 interactions with critical cell cycle regulatory proteins, increased CDK2 activity, and inappropriate entry into S-phase. These findings reveal C/EBPα regulates G1/S cell cycle arrest in response to DNA damage via the control of CRL4(Cdt2) mediated degradation of p21.
Keywords: C/EBPα; C/EBPα, CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α; CRL, Cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases; CRL4Cdt2; DCAF, DDB1/CUL4-associated factor; Cdt2, Cdc10 dependent transcript 2; G1/S DNA damage checkpoint; SCF, Skp, Cullin, F-box containing complex; UVB, ultraviolet B; keratinocytes, p21.
Figures

References
-
- American Cancer Society 2013 Cancer Facts and Figures . Atlanta: American Cancer Society. http://cancer.org.
-
- Brash DE. Sunlight and the onset of skin cancer. Trends Genet 1997; 13:410-4; PMID:9351343; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9525(97)01246-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- de Gruijl FR, van Kranen HJ, Mullenders LH. UV-induced DNA damage, repair, mutations and oncogenic pathways in skin cancer. J Photochem Photobiol 2001; 63:19-27; PMID:11684448; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1011-1344(01)00199-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brash DE, Rudolph JA, Simon JA, Lin A, McKenna GJ, Baden HP, Halperin AJ, Ponten J. A role for sunlight in skin cancer: UV-induced p53 mutations in squamous cell carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1991; 88:10124-8; PMID:1946433; http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.88.22.10124 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kastan MB, Bartek J. Cell-cycle checkpoints and cancer. Nature 2004; 432:316-23; PMID:15549093; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature03097 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
