Vav family exchange factors: an integrated regulatory and functional view
- PMID: 25483299
- PMCID: PMC4601183
- DOI: 10.4161/21541248.2014.973757
Vav family exchange factors: an integrated regulatory and functional view
Abstract
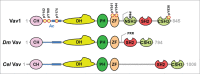
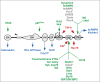
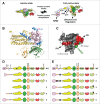
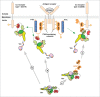
The Vav family is a group of tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated signal transduction molecules hierarchically located downstream of protein tyrosine kinases. The main function of these proteins is to work as guanosine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) for members of the Rho GTPase family. In addition, they can exhibit a variety of catalysis-independent roles in specific signaling contexts. Vav proteins play essential signaling roles for both the development and/or effector functions of a large variety of cell lineages, including those belonging to the immune, nervous, and cardiovascular systems. They also contribute to pathological states such as cancer, immune-related dysfunctions, and atherosclerosis. Here, I will provide an integrated view about the evolution, regulation, and effector properties of these signaling molecules. In addition, I will discuss the pros and cons for their potential consideration as therapeutic targets.
Keywords: Ac, acidic; Ahr, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; CH, calponin homology; CSH3, most C-terminal SH3 domain of Vav proteins; DAG, diacylglycerol; DH, Dbl-homology domain; Dbl-homology; GDP/GTP exchange factors; GEF, guanosine nucleotide exchange factor; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; IP3, inositoltriphosphate; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T-cells; NSH3, most N-terminal SH3 domain of Vav proteins; PH, plekstrin-homology domain; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase; PIP3, phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-triphosphate; PKC, protein kinase C; PKD, protein kinase D; PLC-g, phospholipase C-g; PRR, proline-rich region; PTK, protein tyrosine kinase; Phox, phagocyte oxidase; Rho GTPases; SH2, Src homology 2; SH3, Src homology 3; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; TCR, T-cell receptor; Vav; ZF, zinc finger region; cGMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate; cancer; cardiovascular biology; disease; immunology; nervous system; signaling; therapies.
Figures
References
-
- Henske EP, Short MP, Jozwiak S, Bovey CM, Ramlakhan S, Haines JL, Kwiatkowski DJ. Identification of VAV2 on 9q34 and its exclusion as the tuberous sclerosis gene TSC1. Ann Hum Genet 1995; 59:25-37; PMID:7762982; http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-1809.1995.tb01603.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schuebel KE, Bustelo XR, Nielsen DA, Song BJ, Barbacid M, Goldman D, Lee IJ. Isolation and characterization of murine vav2, a member of the vav family of proto-oncogenes. Oncogene 1996; 13:363-71; PMID:8710375 - PubMed
-
- Bustelo XR. Regulatory and signaling properties of the Vav family. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20:1461-77; PMID:10669724; http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/MCB.20.5.1461-1477.2000 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
