Epithelial junctions and Rho family GTPases: the zonular signalosome
- PMID: 25483301
- PMCID: PMC4601189
- DOI: 10.4161/21541248.2014.973760
Epithelial junctions and Rho family GTPases: the zonular signalosome
Abstract
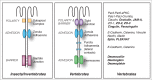
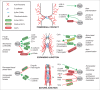
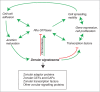
The establishment and maintenance of epithelial cell-cell junctions is crucially important to regulate adhesion, apico-basal polarity and motility of epithelial cells, and ultimately controls the architecture and physiology of epithelial organs. Junctions are supported, shaped and regulated by cytoskeletal filaments, whose dynamic organization and contractility are finely tuned by GTPases of the Rho family, primarily RhoA, Rac1 and Cdc42. Recent research has identified new molecular mechanisms underlying the cross-talk between these GTPases and epithelial junctions. Here we briefly summarize the current knowledge about the organization, molecular evolution and cytoskeletal anchoring of cell-cell junctions, and we comment on the most recent advances in the characterization of the interactions between Rho GTPases and junctional proteins, and their consequences with regards to junction assembly and regulation of cell behavior in vertebrate model systems. The concept of "zonular signalosome" is proposed, which highlights the close functional relationship between proteins of zonular junctions (zonulae occludentes and adhaerentes) and the control of cytoskeletal organization and signaling through Rho GTPases, transcription factors, and their effectors.
Keywords: AJ, adherens junction; AMOT, angiomotin; AMPK, Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase; APC, adenomatous poliposis coli; CD2AP, CD2-associated protein; CGN, cingulin; CGNL1, paracingulin; Cdc42; Cdc42, cell division cycle 42; DLC, deleted in liver cancer; Dbl, diffuse B-cell lymphoma; EPLIN, epithelial protein lost in neoplasm; ERK, extracellular regulated kinase; FERM, four.point.one, ezrin, radixin, moesin; FGD5, FYVE, RhoGEF and PH domain containing 5; GAP, GTPase activating protein; GEF, guanine nucleotide exchange factor; GST, glutathione -S- transferase; JAM = junctional adhesion molecule; MCF-7, Michigan Cancer Foundation - 7; MDCK, Madin Darby Canine Kidney; MKLP1, mitotic kinesin-like protein-1; MRCK, myotonic dystrophy-related Cdc42-binding kinase; MgcRacGAP, male germ cell racGAP; PA, puncta adhaerentia; PAK, p21-activated kinase; PATJ, Pals1 associated tight junction protein; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen; PDZ, Post synaptic density protein (PSD95), Drosophila, disc large tumour suppressor (DlgA), and zonula occludens-1; PLEKHA7, pleckstrin homology domain containing, family A member 7; RICH-1, RhoGAP interacting with CIP4 homologues; ROCK, Rho-associated protein kinase; Rac; Rho; SH3BP1, (SH3 domain 490 binding protein-1); TJ, tight junction; Tbx-3, T-box-3; Tiam, Tumor invasion and metastasis; WASP, Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome Protein; WAVE, WASP family Verprolin-homologous protein; ZA, zonula adhaerens; ZO, zonula occludens; ZONAB, (ZO-1)–associated nucleic acid binding protein.; cytoseleton; epithelium; junctions.
Figures

References
-
- Gonzalez-Mariscal L, Garay E, Lechuga S. Virus interaction with the apical junctional complex. Front Biosci 2009; 14:731-68; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.2741/3276 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vogelmann R, Amieva MR, Falkow S, Nelson WJ. Breaking into the epithelial apical-junctional complex–news from pathogen hackers. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2004; 16:86-93; PMID:15037310; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.ceb.2003.12.002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shin K, Fogg VC, Margolis B. Tight junctions and cell polarity. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2006; 22:207-35; PMID:16771626; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.22.010305.104219 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anderson JM, Van Itallie CM. Physiology and function of the tight junction. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2009; 1:a002584:1-16; PMID:20066090; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1101/cshperspect.a002584 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Franke WW, Rickelt S, Barth M, Pieperhoff S. The junctions that don't fit the scheme: special symmetrical cell-cell junctions of their own kind. Cell Tissue Res 2009; 338:1-17; PMID:19680692; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1007/s00441-009-0849-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
