BAR domain proteins regulate Rho GTPase signaling
- PMID: 25483303
- PMCID: PMC4601494
- DOI: 10.4161/sgtp.28580
BAR domain proteins regulate Rho GTPase signaling
Abstract
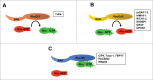
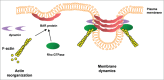
BAR proteins comprise a heterogeneous group of multi-domain proteins with diverse biological functions. The common denominator is the Bin-Amphiphysin-Rvs (BAR) domain that not only confers targeting to lipid bilayers, but also provides scaffolding to mold lipid membranes into concave or convex surfaces. This function of BAR proteins is an important determinant in the dynamic reconstruction of membrane vesicles, as well as of the plasma membrane. Several BAR proteins function as linkers between cytoskeletal regulation and membrane dynamics. These links are provided by direct interactions between BAR proteins and actin-nucleation-promoting factors of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein family and the Diaphanous-related formins. The Rho GTPases are key factors for orchestration of this intricate interplay. This review describes how BAR proteins regulate the activity of Rho GTPases, as well as how Rho GTPases regulate the function of BAR proteins. This mutual collaboration is a central factor in the regulation of vital cellular processes, such as cell migration, cytokinesis, intracellular transport, endocytosis, and exocytosis.
Keywords: BAR domain; F-BAR; Rho GTPases; actin; membrane trafficking.
Figures
References
-
- Qualmann B, Koch D, Kessels MM. Let's go bananas: revisiting the endocytic BAR code. EMBO J 2011; 30:3501-15; PMID:21878992; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2011.266 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- David C, Solimena M, De Camilli P. Autoimmunity in stiff-Man syndrome with breast cancer is targeted to the C-terminal region of human amphiphysin, a protein similar to the yeast proteins, Rvs167 and Rvs161. FEBS Lett 1994; 351:73-9; PMID:8076697; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(94)00826-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang B, Zelhof AC. Amphiphysins: raising the BAR for synaptic vesicle recycling and membrane dynamics. Bin-Amphiphysin-Rvsp. Traffic 2002; 3:452-60; PMID:12047553; http://dx.doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0854.2002.30702.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Peter BJ, Kent HM, Mills IG, Vallis Y, Butler PJ, Evans PR, McMahon HT. BAR domains as sensors of membrane curvature: the amphiphysin BAR structure. Science 2004; 303:495-9; PMID:14645856; http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1092586 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Praefcke GJ, McMahon HT. The dynamin superfamily: universal membrane tubulation and fission molecules? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2004; 5:133-47; PMID:15040446; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrm1313 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
