Effectiveness of interventions that apply new media to improve vaccine uptake and vaccine coverage
- PMID: 25483518
- PMCID: PMC4514191
- DOI: 10.4161/hv.34313
Effectiveness of interventions that apply new media to improve vaccine uptake and vaccine coverage
Abstract
Background: Vaccine-preventable diseases (VPD) are still a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. In high and middle-income settings, immunization coverage is relatively high. However, in many countries coverage rates of routinely recommended vaccines are still below the targets established by international and national advisory committees. Progress in the field of communication technology might provide useful tools to enhance immunization strategies.
Objective: To systematically collect and summarize the available evidence on the effectiveness of interventions that apply new media to promote vaccination uptake and increase vaccination coverage.
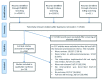
Design: We conducted a systematic literature review. Studies published from January 1999 to September 2013 were identified by searching electronic resources (Pubmed, Embase), manual searches of references and expert consultation. Study setting We focused on interventions that targeted recommended vaccinations for children, adolescents and adults and: (1) aimed at increasing community demand for immunizations, or (2) were provider-based interventions. We limited the study setting to countries that are members of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
Main outcome measures: The primary outcome was a measure of vaccination (vaccine uptake or vaccine coverage). Considered secondary outcomes included willingness to receive immunization, attitudes and perceptions toward vaccination, and perceived helpfulness of the intervention.
Results: Nineteen studies were included in the systematic review. The majority of the studies were conducted in the US (74%, n = 14); 68% (n = 13) of the studies were experimental, the rest having an observational study design. Eleven (58%) reported results on the primary outcome. Retrieved studies explored the role of: text messaging (n.7, 37%), smartphone applications (n.1, 5%), Youtube videos (n.1, 5%), Facebook (n.1, 5%), targeted websites and portals (n.4, 21%), software for physicians and health professionals (n.4, 21%), and email communication (n.1, 5%). There is some evidence that text messaging, accessing immunization campaign websites, using patient-held web-based portals and computerized reminders increase immunization coverage rates. Insufficient evidence is available on the use of social networks, email communication and smartphone applications.
Conclusion: Although there is great potential for improving vaccine uptake and vaccine coverage by implementing programs and interventions that apply new media, scant data are available and further rigorous research - including cost-effectiveness assessments - is needed.
Keywords: communication technology; immunization; interventions; new media; social media; systematic review; vaccine coverage; vaccine preventable diseases; vaccine uptake.
References
-
- WHO. Immunization http://www.who.int/gho/immunization/en/.
-
- WHO. Estimates of disease burden and cost-effectiveness http://www.who.int/immunization/monitoring_surveillance/burden/estimates....
-
- WHO. World Immunization Week http://www.who.int/campaigns/immunization-week/2014/event/en/.
-
- Crosignani P, De Stefani A, Fara GM, Isidori AM, Lenzi A, Liverani CA, Lombardi A, Mennini FS, Palu’ G, Pecorelli S, et al.. Towards the eradication of HPV infection through universal specific vaccination. BMC Public Health 2013; 13:642; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1186/1471-2458-13-642; PMID: 23845195 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pang T... Vaccination in developing countries: problems, challenges and opportunities. Global Perspectives in Health Vol II
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical