The σ enigma: bacterial σ factors, archaeal TFB and eukaryotic TFIIB are homologs
- PMID: 25483602
- PMCID: PMC4581349
- DOI: 10.4161/21541264.2014.967599
The σ enigma: bacterial σ factors, archaeal TFB and eukaryotic TFIIB are homologs
Abstract
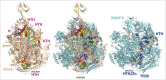
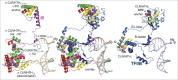
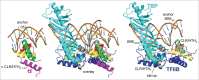
Structural comparisons of initiating RNA polymerase complexes and structure-based amino acid sequence alignments of general transcription initiation factors (eukaryotic TFIIB, archaeal TFB and bacterial σ factors) show that these proteins are homologs. TFIIB and TFB each have two-five-helix cyclin-like repeats (CLRs) that include a C-terminal helix-turn-helix (HTH) motif (CLR/HTH domains). Four homologous HTH motifs are present in bacterial σ factors that are relics of CLR/HTH domains. Sequence similarities clarify models for σ factor and TFB/TFIIB evolution and function and suggest models for promoter evolution. Commitment to alternate modes for transcription initiation appears to be a major driver of the divergence of bacteria and archaea.
Keywords: BRE, TFB/TFIIB recognition element; CLR/HTH, cyclin-like repeat/helix-turn-helix domain; DDRP, DNA-dependent RNA polymerase; DPBB, double psi beta barrel; GTF, general transcription factor; LECA, last eukaryotic common ancestor; LUCA, last universal common ancestor; Ms, Methanocaldococcus sp. FS406-22,; PIF, primordial initiation factor; RDRP, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; RNAP, RNA polymerase; Sc, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; TFB, transcription factor B; TFIIB, transcription factor for RNAP II; factor B, Tt, Thermus thermophilus..
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prokaryotic sigma factors and their transcriptional counterparts in Archaea and Eukarya.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 May;104(10):4289-4302. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10577-0. Epub 2020 Mar 30. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32232532 Review.
-
A model for genesis of transcription systems.Transcription. 2016;7(1):1-13. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2015.1128518. Transcription. 2016. PMID: 26735411 Free PMC article.
-
The basal transcription factors TBP and TFB from the mesophilic archaeon Methanosarcina mazeii: structure and conformational changes upon interaction with stress-gene promoters.J Mol Biol. 2001 Jun 8;309(3):589-603. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.4705. J Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11397082
-
Modulation of RNA polymerase core functions by basal transcription factor TFB/TFIIB.Biochem Soc Symp. 2006;(73):49-58. doi: 10.1042/bss0730049. Biochem Soc Symp. 2006. PMID: 16626286
-
The many faces of the helix-turn-helix domain: transcription regulation and beyond.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2005 Apr;29(2):231-62. doi: 10.1016/j.femsre.2004.12.008. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2005. PMID: 15808743 Review.
Cited by
-
The Possible Crystallization Process in the Origin of Bacteria, Archaea, Viruses, and Mobile Elements.Biology (Basel). 2024 Dec 24;14(1):3. doi: 10.3390/biology14010003. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39857234 Free PMC article.
-
Early Evolution of Transcription Systems and Divergence of Archaea and Bacteria.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 5;8:651134. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.651134. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34026831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution of the genetic code.Transcription. 2021 Feb;12(1):28-53. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2021.1927652. Epub 2021 May 18. Transcription. 2021. PMID: 34000965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nascent RNA sequencing identifies a widespread sigma70-dependent pausing regulated by Gre factors in bacteria.Nat Commun. 2021 Feb 10;12(1):906. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21150-2. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33568644 Free PMC article.
-
A critical role of a plant-specific TFIIB-related protein, BRP1, in salicylic acid-mediated immune response.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jul 30;15:1427916. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1427916. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39139725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Koonin EV, Yutin N. The dispersed archaeal eukaryome and the complex archaeal ancestor of eukaryotes. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect biol 2014; 6:a016188; PMID:24691961; http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a016188 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burton ZF. The old and New testaments of gene regulation: evolution of multi-subunit RNA polymerases and co-evolution of eukaryote complexity with the RNAP II CTD. Transcription 2014; 5; PMID:24802897; http://dx.doi.org/10.4161/trns.28674 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Iyer LM, Koonin EV, Aravind L. Evolutionary connection between the catalytic subunits of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases and eukaryotic RNA-dependent RNA polymerases and the origin of RNA polymerases. BMC Struct Biol 2003; 3:1;PMID:12553882; http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1472-6807-3-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Iyer LM, Aravind L. Insights from the architecture of the bacterial transcription apparatus. J Struct Biol 2012; 179:299–319; PMID:22210308; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2011.12.013 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Feklistov A, Sharon BD, Darst SA, Gross CA. Bacterial sigma factors: a historical, structural, and genomic perspective. Annu Rev Microbiol 2014;68:357–76; PMID:25002089; http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev-micro-092412-155737 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
