Interplay between genetic regulation of phosphate homeostasis and bacterial virulence
- PMID: 25483775
- PMCID: PMC4601331
- DOI: 10.4161/viru.29307
Interplay between genetic regulation of phosphate homeostasis and bacterial virulence
Abstract
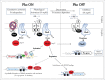
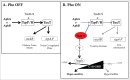
Bacterial pathogens, including those of humans, animals, and plants, encounter phosphate (Pi)-limiting or Pi-rich environments in the host, depending on the site of infection. The environmental Pi-concentration results in modulation of expression of the Pho regulon that allows bacteria to regulate phosphate assimilation pathways accordingly. In many cases, modulation of Pho regulon expression also results in concomitant changes in virulence phenotypes. Under Pi-limiting conditions, bacteria use the transcriptional-response regulator PhoB to translate the Pi starvation signal sensed by the bacterium into gene activation or repression. This regulator is employed not only for the maintenance of bacterial Pi homeostasis but also to differentially regulate virulence. The Pho regulon is therefore not only a regulatory circuit of phosphate homeostasis but also plays an important adaptive role in stress response and bacterial virulence. Here we focus on recent findings regarding the mechanisms of gene regulation that underlie the virulence responses to Pi stress in Vibrio cholerae, Pseudomonas spp., and pathogenic E. coli.
Keywords: Escherichia coli (E. coli); Pho regulon; PhoB; Pseudomonas spp.; Pst; Vibrio cholerae; bacterial pathogens; gene regulation; phosphate limitation; virulence.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The phosphate regulon and bacterial virulence: a regulatory network connecting phosphate homeostasis and pathogenesis.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008 May;32(3):461-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00101.x. Epub 2008 Jan 29. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18248418 Review.
-
The Pho regulon and the pathogenesis of Escherichia coli.Vet Microbiol. 2011 Nov 21;153(1-2):82-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2011.05.043. Epub 2011 Jun 1. Vet Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21700403 Review.
-
Gene regulation by phosphate in enteric bacteria.J Cell Biochem. 1993 Jan;51(1):47-54. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240510110. J Cell Biochem. 1993. PMID: 8432742 Review.
-
Crystal structure of PhoU from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a negative regulator of the Pho regulon.J Struct Biol. 2014 Oct;188(1):22-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2014.08.010. Epub 2014 Sep 8. J Struct Biol. 2014. PMID: 25220976
-
PhoB regulates both environmental and virulence gene expression in Vibrio cholerae.Mol Microbiol. 2010 Sep;77(6):1595-605. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07310.x. Epub 2010 Aug 16. Mol Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20659293 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa Phosphate Transporter PitA (PA4292) Controls Susceptibility to Aminoglycoside Antibiotics by Regulating the Proton Motive Force.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022 Dec 20;66(12):e0099222. doi: 10.1128/aac.00992-22. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022. PMID: 36346250 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying dynamic mechanisms of auto-regulation in Escherichia coli with synthetic promoter in response to varying external phosphate levels.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 14;9(1):2076. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-38223-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30765722 Free PMC article.
-
Tetanus Toxin Synthesis is Under the Control of A Complex Network of Regulatory Genes in Clostridium tetani.Toxins (Basel). 2020 May 15;12(5):328. doi: 10.3390/toxins12050328. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32429286 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of Phosphate Homeostasis Sensitizes Staphylococcus aureus to Nutritional Immunity.Infect Immun. 2020 May 20;88(6):e00102-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00102-20. Print 2020 May 20. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 32205403 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphate Transporter PstSCAB of Campylobacter jejuni Is a Critical Determinant of Lactate-Dependent Growth and Colonization in Chickens.J Bacteriol. 2020 Mar 11;202(7):e00716-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00716-19. Print 2020 Mar 11. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 31932316 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parkinson JS. Signal transduction schemes of bacteria. Cell 1993; 73:857-71; PMID:8098993; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(93)90267-T - DOI - PubMed
-
- Oshima T, Aiba H, Masuda Y, Kanaya S, Sugiura M, Wanner BL, Mori H, Mizuno T. Transcriptome analysis of all two-component regulatory system mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. Mol Microbiol 2002; 46:281-91; PMID:12366850; http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03170.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mizuno T. Compilation of all genes encoding two-component phosphotransfer signal transducers in the genome of Escherichia coli. DNA Res 1997; 4:161-8; PMID:9205844; http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/dnares/4.2.161 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yang C, Huang TW, Wen SY, Chang CY, Tsai SF, Wu WF, Chang CH. Genome-wide PhoB binding and gene expression profiles reveal the hierarchical gene regulatory network of phosphate starvation in Escherichia coli. PLoS One 2012; 7:e47314; PMID:23071782; http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0047314 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hsieh YJ, Wanner BL. Global regulation by the seven-component Pi signaling system. Curr Opin Microbiol 2010; 13:198-203; PMID:20171928; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2010.01.014 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
