Critical role of bioanalytical strategies in investigation of clinical PK observations, a Phase I case study
- PMID: 25484037
- PMCID: PMC4623117
- DOI: 10.4161/mabs.36208
Critical role of bioanalytical strategies in investigation of clinical PK observations, a Phase I case study
Abstract
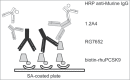
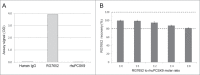
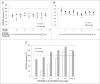
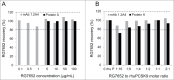
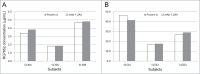
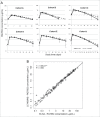
RG7652 is a human immunoglobulin 1 (IgG1) monoclonal antibody (mAb) targeting proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) and is designed for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia. A target-binding enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was developed to measure RG7652 levels in human serum in a Phase I study. Although target-binding assay formats are generally used to quantify free therapeutic, the actual therapeutic species being measured are affected by assay conditions, such as sample dilution and incubation time, and levels of soluble target in the samples. Therefore, in the presence of high concentrations of circulating target, the choice of reagents and assay conditions can have a significant effect on the observed pharmacokinetic (PK) profiles. Phase I RG7652 PK analysis using the ELISA data resulted in a nonlinear dose normalized exposure. An investigation was conducted to characterize the ELISA to determine whether the assay format and reagents may have contributed to the PK observation. In addition, to confirm the ELISA results, a second orthogonal method, liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) using a signature peptide as surrogate, was developed and implemented. A subset of PK samples, randomly selected from half of the subjects in the 6 single ascending dose (SAD) cohorts in the Phase I clinical study, was analyzed with the LC-MS/MS assay, and the data were found to be comparable to the ELISA data. This paper illustrates the importance of reagent characterization, as well as the benefits of using an orthogonal approach to eliminate bioanalytical contributions when encountering unexpected observations.
Keywords: 5, 5′-tetramethylbenzidine;; BSA, bovine serum albumin; CDR, complementarity-determining region; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; HRP, horseradish peroxidase; IS, internal standard; IgG1, immunoglobulin G1; LC-MS/MS; LC-MS/MS, liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry; LDL-c, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDLR, low density lipoprotein receptor; LLOQ, lower limit of quantification; MAD, multiple-ascending dose; MQC, minimum quantifiable concentration; MRM, multiple reaction monitoring; NHS, normal human sera; PBS, phosphate buffered saline; PCSK9, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9;; PD, pharmacodynamics; PK, pharmacokinetics; RG7652; RT, room temperature; S/N, signal-to-noise; SA, streptavidin; SAD, single-ascending dose; SIL, stable isotope-labeled; TMB, 3, 3′; clinical pharmacokinetic assay; enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; mAbs, monoclonal antibodies; proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9; rhuPCSK9, recombinant human PCSK9; signature peptide.
Figures

References
-
- Kwon HJ, Lagace TA, McNutt MC, Horton JD, Deisenhofer J. Molecular basis for LDL receptor recognition by PCSK9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008; 105: 1820-5; PMID:18250299; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1073/pnas.0712064105 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Qian YW, Schmidt RJ, Zhang Y, Chu S, Lin A, Wang H, Wang X, Beyer TP, Bensch WR, Li W, et al. Secreted PCSK9 downregulates low density lipoprotein receptor through receptor-mediated endocytosis. J Lipid Res 2007; 48: 1488-98; PMID:17449864; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1194/jlr.M700071-JLR200 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fischer SK, Yang J, Anand B, Cowan K, Hendricks R, Li J, Nakamura G, Song A. The assay design used for measurement of therapeutic antibody concentrations can affect pharmacokinetic parameters: Case studies. MAbs 2012; 4: 623-31; PMID:22820463; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.4161/mabs.20814 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kuang B, King L, Wang HF. Therapeutic monoclonal antibody concentration monitoring: free or total? Bioanalysis 2010; 2: 1125-40; PMID:21083212; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.4155/bio.10.64 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
