Autophagy in osteoblasts is involved in mineralization and bone homeostasis
- PMID: 25484092
- PMCID: PMC4502694
- DOI: 10.4161/auto.36182
Autophagy in osteoblasts is involved in mineralization and bone homeostasis
Abstract
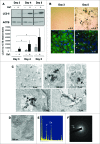
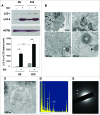
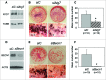
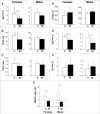
Bone remodeling is a tightly controlled mechanism in which osteoblasts (OB), the cells responsible for bone formation, osteoclasts (OC), the cells specialized for bone resorption, and osteocytes, the multifunctional mechanosensing cells embedded in the bone matrix, are the main actors. Increased oxidative stress in OB, the cells producing and mineralizing bone matrix, has been associated with osteoporosis development but the role of autophagy in OB has not yet been addressed. This is the goal of the present study. We first show that the autophagic process is induced in OB during mineralization. Then, using knockdown of autophagy-essential genes and OB-specific autophagy-deficient mice, we demonstrate that autophagy deficiency reduces mineralization capacity. Moreover, our data suggest that autophagic vacuoles could be used as vehicles in OB to secrete apatite crystals. In addition, autophagy-deficient OB exhibit increased oxidative stress and secretion of the receptor activator of NFKB1 (TNFSF11/RANKL), favoring generation of OC, the cells specialized in bone resorption. In vivo, we observed a 50% reduction in trabecular bone mass in OB-specific autophagy-deficient mice. Taken together, our results show for the first time that autophagy in OB is involved both in the mineralization process and in bone homeostasis. These findings are of importance for mineralized tissues which extend from corals to vertebrates and uncover new therapeutic targets for calcified tissue-related metabolic pathologies.
Keywords: ACP5/TRAP, acid phosphatase 5, tartrate resistant; BECN1, Beclin 1, autophagy-related; BV, bone volume; Baf, bafilomycin A1; Col1A, collagen, type I, α 1; HRTEM, high resolution transmission electron microscopy; MAP1LC3 (LC3), microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3; OB, osteoblast; OC, osteoclast; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; RNA, ribonucleic acid; RUNX2, runt-related transcription factor 2; SAED, selected area electron diffraction; SPP1/OPN, secreted phosphoprotein 1; TNFSF11/RANKL, tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 11; TUBB, tubulin, beta; TV, total volume; autophagy; bone remodeling; mineralization; osteoblast.
Figures


References
-
- Raggatt LJ, Partridge NC. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of bone remodeling. J Biol Chem 2010; 285:25103-8; PMID:20501658; http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R109.041087 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kular J, Tickner J, Chim SM, Xu J. An overview of the regulation of bone remodelling at the cellular level. Clin Biochem 2012; 45:863-73; PMID:22465238; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2012.03.021 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Manolagas SC. From estrogen-centric to aging and oxidative stress: a revised perspective of the pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev 2010; 31:266-300; PMID:20051526; http://dx.doi.org/10.1210/er.2009-0024 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Levine B, Kroemer G. Autophagy in the pathogenesis of disease. Cell 2008; 132:27-42; PMID:18191218; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.018 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM, Klionsky DJ. Autophagy fights disease through cellular self-digestion. Nature 2008; 451:1069-75; PMID:18305538; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature06639 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
