Preliminary crystallographic analysis of Xyn52B2, a GH52 β-D-xylosidase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus T6
- PMID: 25484225
- PMCID: PMC4259239
- DOI: 10.1107/S2053230X14023887
Preliminary crystallographic analysis of Xyn52B2, a GH52 β-D-xylosidase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus T6
Abstract
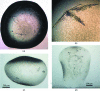
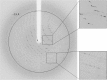
Geobacillus stearothermophilus T6 is a thermophilic bacterium that possesses an extensive hemicellulolytic system, including over 40 specific genes that are dedicated to this purpose. For the utilization of xylan, the bacterium uses an extracellular xylanase which degrades xylan to decorated xylo-oligomers that are imported into the cell. These oligomers are hydrolyzed by side-chain-cleaving enzymes such as arabinofuranosidases, acetylesterases and a glucuronidase, and finally by an intracellular xylanase and a number of β-xylosidases. One of these β-xylosidases is Xyn52B2, a GH52 enzyme that has already proved to be useful for various glycosynthesis applications. In addition to its demonstrated glycosynthase properties, interest in the structural aspects of Xyn52B2 stems from its special glycoside hydrolase family, GH52, the structures and mechanisms of which are only starting to be resolved. Here, the cloning, overexpression, purification and crystallization of Xyn52B2 are reported. The most suitable crystal form that has been obtained belonged to the orthorhombic P212121 space group, with average unit-cell parameters a = 97.7, b = 119.1, c = 242.3 Å. Several X-ray diffraction data sets have been collected from flash-cooled crystals of this form, including the wild-type enzyme (3.70 Å resolution), the E335G catalytic mutant (2.95 Å resolution), a potential mercury derivative (2.15 Å resolution) and a selenomethionine derivative (3.90 Å resolution). These data are currently being used for detailed three-dimensional structure determination of the Xyn52B2 protein.
Keywords: GH52; Geobacillus stearothermophilus; SAD data collection; enzymatic glycosynthesis; glycoside hydrolase; glycosynthase; selenomethionine; xylan utilization; xylobiose; xylose; xylosidase.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cloning, purification and preliminary crystallographic analysis of Ara127N, a GH127 β-L-arabinofuranosidase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus T6.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2014 Aug;70(Pt 8):1038-45. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X14012680. Epub 2014 Jul 23. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2014. PMID: 25084377 Free PMC article.
-
A novel β-xylosidase structure from Geobacillus thermoglucosidasius: the first crystal structure of a glycoside hydrolase family GH52 enzyme reveals unpredicted similarity to other glycoside hydrolase folds.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014 May;70(Pt 5):1366-74. doi: 10.1107/S1399004714002788. Epub 2014 Apr 30. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014. PMID: 24816105
-
Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of GanB, a GH42 intracellular β-galactosidase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2013 Oct;69(Pt 10):1114-9. doi: 10.1107/S1744309113023609. Epub 2013 Sep 28. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2013. PMID: 24100561 Free PMC article.
-
Purification, crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of Gan1D, a GH1 6-phospho-β-galactosidase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus T1.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2014 Feb;70(Pt 2):225-31. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X13034778. Epub 2014 Jan 21. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2014. PMID: 24637762 Free PMC article.
-
Structures, Biochemical Characteristics, and Functions of β-Xylosidases.J Agric Food Chem. 2023 May 31;71(21):7961-7976. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c01425. Epub 2023 May 16. J Agric Food Chem. 2023. PMID: 37192316 Review.
References
-
- Almog, O., Greenblatt, H. M., Spungin, A., Ben-Meir, D., Blumberg, S. & Shoham, G. (1993). J. Mol. Biol. 230, 342–344. - PubMed
-
- Almog, O., Klein, D., Braun, S. & Shoham, G. (1994). J. Mol. Biol. 235, 760–762. - PubMed
-
- Bar, M., Golan, G., Nechama, M., Zolotnitsky, G., Shoham, Y. & Shoham, G. (2004). Acta Cryst. D60, 545–549. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

