Crystal structure of difenoconazole
- PMID: 25484812
- PMCID: PMC4257337
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814022429
Crystal structure of difenoconazole
Abstract
In the title compound difenoconazole [systematic name: 1-({2-[2-chloro-4-(4-chloro-phen-oxy)phen-yl]-4-methyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-yl}meth-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole], C19H17Cl2N3O3, the dihedral angle between the planes of the 4-chloro-phenyl and 2-chloro-phenyl rings is 79.34 (9)°, while the dihedral angle between the planes of the triazole ring and the dioxolanyl group is 59.45 (19)°. In the crystal, pairs of C-H⋯N hydrogen bonds link adjacent mol-ecules, forming dimers with R 2 (2)(6) loops. In addition, the dimers are linked by C-H⋯O hydrogen bonds, resulting in a three-dimensional architecture. Disorder was modeled for one C atom of the dioxolanyl group over two sets of sites with an occupancy ratio of 0.566 (17):0.434 (17).
Keywords: crystal structure; difenoconazole; hydrogen bonds; triazole fungicide.
Figures

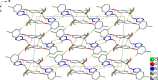
References
-
- Brandenburg, K. (2010). DIAMOND. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
-
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Dong, F., Li, J., Chankvetadze, B., Cheng, Y., Xu, J., Liu, X., Li, Y., Chen, X., Bertucci, C., Tedesco, D., Zanasi, R. & Zheng, Y. (2013). Environ. Sci. Technol. 47, 3386–3394. - PubMed
-
- Mu, X., Pang, S., Sun, X., Gao, J., Chen, J., Chen, X., Li, X. & Wang, C. (2013). Environ. Pollut. 175, 147–157. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
