Acute exposure to a precursor of advanced glycation end products induces a dual effect on the rat pancreatic islet function
- PMID: 25484898
- PMCID: PMC4248554
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/378284
Acute exposure to a precursor of advanced glycation end products induces a dual effect on the rat pancreatic islet function
Abstract
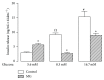
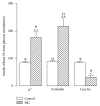
Aim. Chronic diseases are the leading cause of death worldwide. Advanced glycation end products, known as AGEs, are a major risk factor for diabetes onset and maintenance. Methylglyoxal (MG), a highly reactive metabolite of glucose, is a precursor for the generation of endogenous AGEs. Methods. In this current study we incubated in vitro pancreatic islets from adult rats in absence or presence of MG (10 μmol/l) with different concentrations of glucose and different metabolic components (acetylcholine, epinephrine, potassium, forskolin, and leucine). Results. Different effects of MG on insulin secretion were evidenced. In basal glucose stimulation (5.6 mM), MG induced a significant (P < 0.05) increase of insulin secretion. By contrast, in higher glucose concentrations (8.3 mM and 16.7 mM), MG significantly inhibited insulin secretion (P < 0.05). In the presence of potassium, forskolin, and epinephrine, MG enhanced insulin secretion (P < 0.05), while when it was incubated with acetylcholine and leucine, MG resulted in a decrease of insulin secretion (P < 0.05). Conclusion. We suggest that MG modulates the secretion activity of beta-cell depending on its level of stimulation by other metabolic factors. These results provide insights on a dual acute effect of MG on the pancreatic cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Advanced glycation end products impair glucose-induced insulin secretion from rat pancreatic β-cells.J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2014 Feb;21(2):134-41. doi: 10.1002/jhbp.12. Epub 2013 Jun 20. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2014. PMID: 23798335
-
Long-term treatment with atrial natriuretic peptide inhibits ATP production and insulin secretion in rat pancreatic islets.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Mar;300(3):E435-44. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00398.2010. Epub 2010 Oct 19. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2011. PMID: 20959527
-
High glucose-induced impairment in insulin secretion is associated with reduction in islet glucokinase in a mouse model of susceptibility to islet dysfunction.J Mol Endocrinol. 2005 Aug;35(1):39-48. doi: 10.1677/jme.1.01720. J Mol Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 16087720
-
Pancreatic Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone and Mechanism of Insulin Secretion.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(1):378-384. doi: 10.1159/000494013. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30286449 Review.
-
Effects of prolonged glucose stimulation on pancreatic beta cells: from increased sensitivity to desensitization.Acta Diabetol. 1996 Dec;33(4):253-6. doi: 10.1007/BF00571559. Acta Diabetol. 1996. PMID: 9033963 Review.
Cited by
-
Dicarbonyl Stress at the Crossroads of Healthy and Unhealthy Aging.Cells. 2019 Jul 19;8(7):749. doi: 10.3390/cells8070749. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31331077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental Contaminants and Pancreatic Beta-Cells.J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2016 Sep 1;8(3):257-63. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.2812. Epub 2016 Apr 18. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27087124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inulin Supplementation Lowered the Metabolic Defects of Prolonged Exposure to Chlorpyrifos from Gestation to Young Adult Stage in Offspring Rats.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 19;11(10):e0164614. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164614. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27760213 Free PMC article.
-
Glyoxalase 1 knockdown induces age-related β-cell dysfunction and glucose intolerance in mice.EMBO Rep. 2022 Jul 5;23(7):e52990. doi: 10.15252/embr.202152990. Epub 2022 May 27. EMBO Rep. 2022. PMID: 35620868 Free PMC article.
-
Stevia Nonsweetener Fraction Displays an Insulinotropic Effect Involving Neurotransmission in Pancreatic Islets.Int J Endocrinol. 2018 Apr 29;2018:3189879. doi: 10.1155/2018/3189879. eCollection 2018. Int J Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29853880 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Danaei G., Finucane M. M., Lu Y., Singh G. M., Cowan M. J., Paciorek C. J., Lin J. K., Farzadfar F., Khang Y.-H., Stevens G. A., Rao M., Ali M. K., Riley L. M., Robinson C. A., Ezzati M. National, regional, and global trends in fasting plasma glucose and diabetes prevalence since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 370 country-years and 2·7 million participants. The Lancet. 2011;378(9785):31–40. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60679-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wells-Knecht K. J., Zyzak D. V., Litchfield J. E., Thorpe S. R., Baynes J. W. Mechanism of autoxidative glycosylation: identification of glyoxal and arabinose as intermediates in the autoxidative modification of proteins by glucose. Biochemistry. 1995;34(11):3702–3709. doi: 10.1021/bi00011a027. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

