The arrowhead ministernotomy with rigid sternal plate fixation: a minimally invasive approach for surgery of the ascending aorta and aortic root
- PMID: 25485148
- PMCID: PMC4251070
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/681371
The arrowhead ministernotomy with rigid sternal plate fixation: a minimally invasive approach for surgery of the ascending aorta and aortic root
Abstract
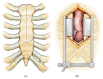
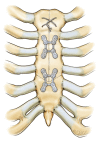
Background. Ministernotomy incisions have been increasingly used in a variety of settings. We describe a novel approach to ministernotomy using arrowhead incision and rigid sternal fixation with a standard sternal plating system. Methods. A small, midline, vertical incision is made from the midportion of the manubrium to a point just above the 4th intercostal mark. The sternum is opened in the shape of an inverted T using two oblique horizontal incisions from the midline to the sternal edges. At the time of chest closure, the three bony segments are aligned and approximated, and titanium plates (Sternalock, Jacksonville, Florida) are used to fix the body of the sternum back together. Results. This case series includes 11 patients who underwent arrowhead ministernotomy with rigid sternal plate fixation for aortic surgery. The procedures performed were axillary cannulation (n = 2), aortic root replacement (n = 3), valve sparing root replacement (n = 3), and replacement of the ascending aorta (n = 11) and/or hemiarch (n = 2). Thirty-day mortality was 0%; there were no conversions, strokes, or sternal wound infections. Conclusions. Arrowhead ministernotomy with rigid sternal plate fixation is an adequate minimally invasive approach for surgery of the ascending aorta and aortic root.
Figures
References
-
- Chiu K. M., Chen R. J., Lin T. Y., Chen J. S., Huang J. H., Huang C. Y., Chu S. H. Right mini-parasternotomy may be a good minimally invasive alternative to full sternotomy for cardiac valve operations-a propensity-adjusted analysis. The Journal of Cardiovascular Surgery. 2014 - PubMed
-
- Yan L., Zhou Z.-C., Li H.-P., Lin M., Wang H.-T., Zhao Z.-W., Gao Q.-Y., Ge J.-J. Right vertical infra-axillary mini-incision for repair of simple congenital heart defects: a matched-pair analysis. European Journal Cardio-Thoracic Surgery. 2013;43(1):136–141. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezs280. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources