Reference values for interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 in cord blood of healthy term neonates and their association with stress-related perinatal factors
- PMID: 25485809
- PMCID: PMC4259323
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114109
Reference values for interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 in cord blood of healthy term neonates and their association with stress-related perinatal factors
Abstract
Background: Automated interleukin assays are promising diagnostic aids for early-onset neonatal sepsis, however, reference values for healthy term neonates are incompletely known. The goal of this study is to determine reference values for interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-8 (IL-8) in cord blood of healthy term neonates.
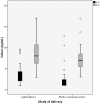
Methods and findings: Women were recruited from April 2012 to August 2012. IL-6 and IL-8 levels were measured using an automated immunometric assay (Immulite) in cord blood of 93 healthy term newborns, 60 of them were born via vaginal delivery and 33 by elective caesarean section (ECS). A mean value for IL-8 of 8.1 ± 3.0 pg/mL was found in cord blood of healthy term neonates, which apply to both vaginal delivery and ECS. Regarding IL-6, two values apply. For vaginal delivery, a median value of 3.3 pg/mL (range, <2 to 9.53 pg/mL) was found, while for ECS, a median value of <2 pg/mL (range, <2 to 48 pg/mL) applies.
Conclusions: We propose a reference value of <14.1 pg/mL for IL-8 (mean + 2SD), applying to vaginally delivered and ECS-delivered healthy term newborns. From a clinical point of view, we also propose one reference value for IL-6 to be applied to vaginally delivered and ECS-delivered healthy term newborns, which is <10.2 pg/mL (97.5th percentile total group). These values have to be validated in larger cohorts of neonates, inclusive of those with and without early-onset neonatal sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Haque KN (2005) Definitions of bloodstream infection in the newborn. Pediatr Crit Care Med: 6(3 Suppl): S45–9. - PubMed
-
- Cernada M, Badia N, Modesto V, Alonso R, Mejias A, et al. (2012) Cord blood interleukin-6 as a predictor of early-onset neonatal sepsis. Acta Paediatr 101(5):e203–7. - PubMed
-
- Benitz WE, Han MY, Madan A, Ramachandra P (1998) Serial serum C-reactive protein levels in the diagnosis of neonatal infection. Pediatrics 102(4):E41. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous