Auricle injury due to human bite - A rare case report and review literature
- PMID: 25485846
- PMCID: PMC4337930
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2014.11.064
Auricle injury due to human bite - A rare case report and review literature
Abstract
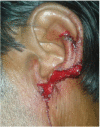
Traumatic auricular amputation due to human bite is not a common event. Bite wounds are always considered to be complex injuries contaminated with unique poly-microbial inoculum. Human bites are as serious as animal bites because they induce a higher incidence of infectious complications. In bite wounds to the face, infectious complications can create more difficulties than the initial tissue damage itself for the task of restoring an esthetic appearance. In this case report a young male patient had ear lobule injury on interpersonal violence and amputation of ear lobule results. Due to delay in presentation and high chances of infection wound healing by secondary intention achieved.
Keywords: Contamination; Ear injury; Human bite.
Copyright © 2014. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Management of facial bite wounds.Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2009 May;21(2):247-57, vii. doi: 10.1016/j.coms.2008.12.009. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2009. PMID: 19348991 Review.
-
Management of facial bite wounds.Dent Clin North Am. 2009 Oct;53(4):691-705, vi. doi: 10.1016/j.cden.2009.08.005. Dent Clin North Am. 2009. PMID: 19958906 Review.
-
Maxillofacial injuries due to animal bites.J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2015 Jun;14(2):142-53. doi: 10.1007/s12663-013-0593-5. Epub 2013 Oct 10. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2015. PMID: 26028828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An unexpected presentation of a traumatic wound on the lower lip: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2014 Sep 7;8:298. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-8-298. J Med Case Rep. 2014. PMID: 25196423 Free PMC article.
-
A Rare Presentation of Donkey Bites Involving the Cheek and Ear: A Case Report and Literature Review.Cureus. 2023 Apr 11;15(4):e37446. doi: 10.7759/cureus.37446. eCollection 2023 Apr. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37182069 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
HUMAN BITE INJURIES ON THE JOS PLATEAU.J West Afr Coll Surg. 2016 Apr-Jun;6(2):1-19. J West Afr Coll Surg. 2016. PMID: 28344944 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pribaz J.J., Crespo L.D., Orgill D.P., Pousti T.J., Bartlett R.A. Ear replantation without microsurgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997;99(7):1868–1872. - PubMed
-
- Nath R.K., Kraemer B.A., Azizzadeh A. Complete ear replantation without venous anastomosis. Microsurgery. 1998;18:282–285. - PubMed
-
- Kind G.M., Buncke G.M., Placik O.J., Jansen D.A., D’ Amore T., Bunche H.J., Jr. Total ear replantation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997;99(7):1858–1867. - PubMed
-
- Mello-Filho F.V., Mamede R.C.M., Koury A.P. Use of a platysma myocutaneous flap for the reimplantation of a severed ear: experience with five cases. Sao Paulo Med J. 1999;117(5):218–223. - PubMed
-
- Maral T., Borman H. Reconstruction of the upper portion of the ear by using an ascending helix free flap from the opposite ear. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000;105(5):1754–1757. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources