μ-Opioid receptor 6-transmembrane isoform: A potential therapeutic target for new effective opioids
- PMID: 25485963
- PMCID: PMC4646084
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2014.11.009
μ-Opioid receptor 6-transmembrane isoform: A potential therapeutic target for new effective opioids
Abstract
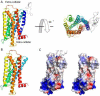
The μ-opioid receptor (MOR) is the primary target for opioid analgesics. MOR induces analgesia through the inhibition of second messenger pathways and the modulation of ion channels activity. Nevertheless, cellular excitation has also been demonstrated, and proposed to mediate reduction of therapeutic efficacy and opioid-induced hyperalgesia upon prolonged exposure to opioids. In this mini-perspective, we review the recently identified, functional MOR isoform subclass, which consists of six transmembrane helices (6 TM) and may play an important role in MOR signaling. There is evidence that 6 TM MOR signals through very different cellular pathways and may mediate excitatory cellular effects rather than the classic inhibitory effects produced by the stimulation of the major (7 TM) isoform. Therefore, the development of 6 TM and 7 TM MOR selective compounds represents a new and exciting opportunity to better understand the mechanisms of action and the pharmacodynamic properties of a new class of opioids.
Keywords: 6TM MOR isoform; Drug discovery; Review; μ-Opioid receptor.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural and functional interactions between six-transmembrane μ-opioid receptors and β2-adrenoreceptors modulate opioid signaling.Sci Rep. 2015 Dec 11;5:18198. doi: 10.1038/srep18198. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26657998 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Regulation of 6- and 7-Transmembrane Helix Variants of μ-Opioid Receptor in Response to Morphine Stimulation.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 10;10(11):e0142826. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142826. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26554831 Free PMC article.
-
Opioid-induced redistribution of 6TM and 7TM μ opioid receptors: A hypothesized mechanistic facilitator model of opioid-induced hyperalgesia.Pharmacol Rep. 2016 Aug;68(4):686-91. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2016.03.003. Epub 2016 Mar 19. Pharmacol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27116700 Review.
-
A novel alternatively spliced isoform of the mu-opioid receptor: functional antagonism.Mol Pain. 2010 Jun 2;6:33. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-6-33. Mol Pain. 2010. PMID: 20525224 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism of μ-opioid receptor (MOR)-TRPV1 crosstalk in TRPV1 activation involves morphine anti-nociception, tolerance and dependence.Channels (Austin). 2015;9(5):235-43. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2015.1069450. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Channels (Austin). 2015. PMID: 26176938 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural and functional interactions between six-transmembrane μ-opioid receptors and β2-adrenoreceptors modulate opioid signaling.Sci Rep. 2015 Dec 11;5:18198. doi: 10.1038/srep18198. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26657998 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Regulation of 6- and 7-Transmembrane Helix Variants of μ-Opioid Receptor in Response to Morphine Stimulation.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 10;10(11):e0142826. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142826. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26554831 Free PMC article.
-
Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia and Tolerance Are Driven by HCN Ion Channels.J Neurosci. 2024 Feb 7;44(6):e1368232023. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1368-23.2023. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38124021 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous and Exogenous Opioids in Pain.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2018 Jul 8;41:453-473. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-080317-061522. Epub 2018 May 31. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29852083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of catechol-O-methyltransferase (rs4680) single-nucleotide polymorphism on opioid-induced hyperalgesia in adults with chronic pain.Mol Pain. 2019 Jan-Dec;15:1744806919848929. doi: 10.1177/1744806919848929. Mol Pain. 2019. PMID: 31041874 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ballantyne JC, Shin NS. Efficacy of opioids for chronic pain: a review of the evidence. Clin. J. Pain. 2008;24:469–478. - PubMed
- Chang G, Chen L, Mao J. Opioid tolerance and hyperalgesia. Med. Clin. North Am. 2007;91:199–211. - PubMed
- Kim SH, Stoicea N, Soghomonyan S, Bergese SD. Intraoperative use of remifentanil and opioid induced hyperalgesia/acute opioid tolerance: systematic review. Front. Pharmacol. 2014;108(5):1–9. - PMC - PubMed
- Middleton C, Harden Acquired pharmaco-dynamic opioid tolerance: a concept analysis. J. J. Adv. Nurs. 2014;70(2):272–281. - PubMed
-
- Lee M, Silverman SM, Hansen H, Patel VB, Manchikanti L. A comprehensive review of opioid-induced hyperalgesia. Pain Physician. 2011;14(2):145–161. - PubMed
- Low Y, Clarke CF, Huh BK. Opioid-induced hyperalgesia: a review of epidemiology, mechanisms and management. Singapore Med. J. 2012;53(5):357–360. - PubMed
- Raehal KM, Schmid CL, Groer CE, Bohn LM. Functional selectivity at the μ-opioid receptor; implications for understanding opioid analgesia and tolerance. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011;63(4):1001–1019. - PMC - PubMed
- Morgan MM, Christie MJ. Analysis of opioid efficacy, tolerance, addiction and dependence from cell culture to human. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011;164(4):1322–1334. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chu LF, Angst MS, Clark D. Opioid-induced hyperalgesia in humans: molecular mechanisms and clinical considerations. Clin. J. Pain. 2008;24:479–496. - PubMed
-
- Crain SM, Shen KF. Antagonists of excitatory opioid receptor functions enhance morphine's analgesic potency and attenuate opioid tolerance/dependence liability. Pain. 2000;84:121–131. - PubMed
-
- North RA. Membrane conductances and opioid receptor subtypes. NIDA Res. Monogr. 1986;71:81–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T90 DE021986/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- G237818/CERC32151/CIHR/Canadian Institutes of Health Research/Canada
- R01-DE16558/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE016558/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R41DA032293-01/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- 1T90DE021986-01/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM080742/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K12 DE022793/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DE017018/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS045685/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R41 DA032293/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM080742/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS041670/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-DE017018/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

