Exposure to mitochondrial genotoxins and dopaminergic neurodegeneration in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 25486066
- PMCID: PMC4259338
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114459
Exposure to mitochondrial genotoxins and dopaminergic neurodegeneration in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
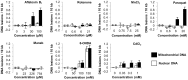
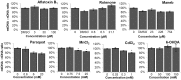
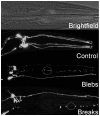
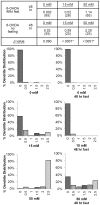
Neurodegeneration has been correlated with mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) damage and exposure to environmental toxins, but causation is unclear. We investigated the ability of several known environmental genotoxins and neurotoxins to cause mtDNA damage, mtDNA depletion, and neurodegeneration in Caenorhabditis elegans. We found that paraquat, cadmium chloride and aflatoxin B1 caused more mitochondrial than nuclear DNA damage, and paraquat and aflatoxin B1 also caused dopaminergic neurodegeneration. 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) caused similar levels of mitochondrial and nuclear DNA damage. To further test whether the neurodegeneration could be attributed to the observed mtDNA damage, C. elegans were exposed to repeated low-dose ultraviolet C radiation (UVC) that resulted in persistent mtDNA damage; this exposure also resulted in dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Damage to GABAergic neurons and pharyngeal muscle cells was not detected. We also found that fasting at the first larval stage was protective in dopaminergic neurons against 6-OHDA-induced neurodegeneration. Finally, we found that dopaminergic neurons in C. elegans are capable of regeneration after laser surgery. Our findings are consistent with a causal role for mitochondrial DNA damage in neurodegeneration, but also support non mtDNA-mediated mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of reduced mitochondrial DNA content on secondary mitochondrial toxicant exposure in Caenorhabditis elegans.Mitochondrion. 2016 Sep;30:255-64. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2016.08.014. Epub 2016 Aug 23. Mitochondrion. 2016. PMID: 27566481 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Defects in Mitochondrial Dynamics in Caenorhabditis elegans Impact Ultraviolet C Radiation- and 6-hydroxydopamine-Induced Neurodegeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 29;20(13):3202. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133202. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31261893 Free PMC article.
-
The tobacco-specific nitrosamine 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK) induces mitochondrial and nuclear DNA damage in Caenorhabditis elegans.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2014 Jan;55(1):43-50. doi: 10.1002/em.21815. Epub 2013 Sep 7. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2014. PMID: 24014178
-
The Caenorhabditis elegans dopaminergic system: opportunities for insights into dopamine transport and neurodegeneration.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2003;43:521-44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.43.100901.135934. Epub 2002 Jan 10. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2003. PMID: 12415122 Review.
-
Mitochondria and mitochondrial DNA as relevant targets for environmental contaminants.Toxicology. 2017 Nov 1;391:100-108. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2017.06.012. Epub 2017 Jun 26. Toxicology. 2017. PMID: 28655544 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuronal responses to stress and injury in C. elegans.FEBS Lett. 2015 Jun 22;589(14):1644-52. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.05.005. Epub 2015 May 13. FEBS Lett. 2015. PMID: 25979176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling Parkinson's Disease in C. elegans.J Parkinsons Dis. 2018;8(1):17-32. doi: 10.3233/JPD-171258. J Parkinsons Dis. 2018. PMID: 29480229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deficiencies in mitochondrial dynamics sensitize Caenorhabditis elegans to arsenite and other mitochondrial toxicants by reducing mitochondrial adaptability.Toxicology. 2017 Jul 15;387:81-94. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2017.05.018. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Toxicology. 2017. PMID: 28602540 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical effects of chemical exposures on mitochondrial function.Toxicology. 2017 Nov 1;391:90-99. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2017.07.009. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Toxicology. 2017. PMID: 28757096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple metabolic changes mediate the response of Caenorhabditis elegans to the complex I inhibitor rotenone.Toxicology. 2021 Jan 15;447:152630. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2020.152630. Epub 2020 Nov 11. Toxicology. 2021. PMID: 33188857 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schmidt CW (2010) Mito-Conundrum: Unraveling Environmental Effects on Mitochondria. Environ Health Perspect 118.
-
- Shaughnessy DT, Worth L Jr, Lawler CP, McAllister KA, Longley MJ, et al. (2010) Meeting report: Identification of biomarkers for early detection of mitochondrial dysfunction. Mitochondrion 10:579–581. - PubMed
-
- Bedard LL, Massey TE (2006) Aflatoxin B1-induced DNA damage and its repair. Cancer Lett 241:174–183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

