DNA end resection is needed for the repair of complex lesions in G1-phase human cells
- PMID: 25486192
- PMCID: PMC4615131
- DOI: 10.4161/15384101.2015.941743
DNA end resection is needed for the repair of complex lesions in G1-phase human cells
Abstract
Repair of DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) is influenced by the chemical complexity of the lesion. Clustered lesions (complex DSBs) are generally considered more difficult to repair and responsible for early and late cellular effects after exposure to genotoxic agents. Resection is commonly used by the cells as part of the homologous recombination (HR) pathway in S- and G2-phase. In contrast, DNA resection in G1-phase may lead to an error-prone microhomology-mediated end joining. We induced DNA lesions with a wide range of complexity by irradiation of mammalian cells with X-rays or accelerated ions of different velocity and mass. We found replication protein A (RPA) foci indicating DSB resection both in S/G2- and G1-cells, and the fraction of resection-positive cells correlates with the severity of lesion complexity throughout the cell cycle. Besides RPA, Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related (ATR) was recruited to complex DSBs both in S/G2- and G1-cells. Resection of complex DSBs is driven by meiotic recombination 11 homolog A (MRE11), CTBP-interacting protein (CtIP), and exonuclease 1 (EXO1) but seems not controlled by the Ku heterodimer or by phosphorylation of H2AX. Reduced resection capacity by CtIP depletion increased cell killing and the fraction of unrepaired DSBs after exposure to densely ionizing heavy ions, but not to X-rays. We conclude that in mammalian cells resection is essential for repair of complex DSBs in all phases of the cell-cycle and targeting this process sensitizes mammalian cells to cytotoxic agents inducing clustered breaks, such as in heavy-ion cancer therapy.
Keywords: ATM, Ataxia telangiectasia mutated; ATR, Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related; BLM, Bloom syndrome protein; BRCA1, breast cancer 1, early onset; CENP-F, centromere protein F; CtIP; CtIP, CTBP-interacting protein; DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; DSB, double strand break; EXO1; EXO1, exonuclease 1; FCS, fetal calf serum; HR, homologous recombination; IR, ionizing radiation; LET, linear energy transfer; MEF, mouse embryonic fibroblasts; MMEJ, microhomology-mediated end joining; MRE11; MRE11, meiotic recombination 11 homolog A; NHEJ, none homologous end joining; PARP, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase; RAD51, DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1; RPA, replication protein A; WRN, Werner syndrome; complex DNA damage; double-strand break repair; kd, knockdown; resection in G1-phase; siRNA, small interfering RNA; ssDNA, single stranded DNA; wt, wild-type.
Figures
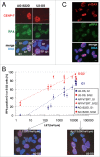
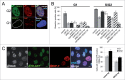
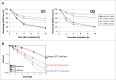
Comment in
-
Complex DSBs: A need for resection.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(24):3796-7. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.986630. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 25495899 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Goodhead DT, Fifth Warren K. Sinclair keynote address: issues in quantifying the effects of low-level radiation. HealthPhys 2009; 97:394–406; PMID: 19820449; http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/HP.0b013e3181ae8acf - DOI - PubMed
-
- Asaithamby A, Hu B, Chen DJ. Unrepaired clustered DNA lesions induce chromosome breakage in human cells. Proc Natl Acad SciUSA 2011; 108:8293–8; PMID: 21527720; http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1016045108 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Goodarzi AA, Jeggo PA. The repair and signaling responses to DNA double-strand breaks. AdvGenet 2013; 82:1–45; PMID: 23721719; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-407676-1.00001-9 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mao Z, Bozzella M, Seluanov A, Gorbunova V. DNA repair by nonhomologous end joining and homologous recombination during cell cycle in human cells. CellCycle 2008; 7:2902–6; PMID: 18769152; http://dx.doi.org/10.4161/cc.7.18.6679 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beucher A, Birraux J, Tchouandong L, Barton O, Shibata A, Conrad S, Goodarzi AA, Krempler A, Jeggo PA, Lobrich M.. ATM and Artemis promote homologous recombination of radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks in G2. EmboJ 2009; 28:3413–27; PMID: 19779458; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2009.276 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
