Flippases and scramblases in the plasma membrane
- PMID: 25486557
- PMCID: PMC4613456
- DOI: 10.4161/15384101.2014.962865
Flippases and scramblases in the plasma membrane
Figures
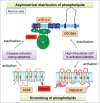
Comment on
-
Caspase-mediated cleavage of phospholipid flippase for apoptotic phosphatidylserine exposure.Science. 2014 Jun 6;344(6188):1164-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1252809. Science. 2014. PMID: 24904167
References
-
- Leventis PA, et al. Annu Rev Biophys 2010; 39:407-27; PMID:20192774; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1146/annurev.biophys.093008.131234 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Suzuki J, et al. Science 2013; 341:403-6; PMID:23845944; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1126/science.1236758 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Suzuki J, et al. Nature 2010; 468:834-8; PMID:21107324; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/nature09583 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Suzuki J, et al. J Biol Chem 2013; 288:13305-16; PMID:23532839; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1074/jbc.M113.457937 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Segawa K, et al. Science 2014; 344:1164-8; PMID:24904167; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1126/science.1252809 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
