A PP1-PP2A phosphatase relay controls mitotic progression
- PMID: 25487150
- PMCID: PMC4338534
- DOI: 10.1038/nature14019
A PP1-PP2A phosphatase relay controls mitotic progression
Abstract
The widespread reorganization of cellular architecture in mitosis is achieved through extensive protein phosphorylation, driven by the coordinated activation of a mitotic kinase network and repression of counteracting phosphatases. Phosphatase activity must subsequently be restored to promote mitotic exit. Although Cdc14 phosphatase drives this reversal in budding yeast, protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) and protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) activities have each been independently linked to mitotic exit control in other eukaryotes. Here we describe a mitotic phosphatase relay in which PP1 reactivation is required for the reactivation of both PP2A-B55 and PP2A-B56 to coordinate mitotic progression and exit in fission yeast. The staged recruitment of PP1 (the Dis2 isoform) to the regulatory subunits of the PP2A-B55 and PP2A-B56 (B55 also known as Pab1; B56 also known as Par1) holoenzymes sequentially activates each phosphatase. The pathway is blocked in early mitosis because the Cdk1-cyclin B kinase (Cdk1 also known as Cdc2) inhibits PP1 activity, but declining cyclin B levels later in mitosis permit PP1 to auto-reactivate. PP1 first reactivates PP2A-B55; this enables PP2A-B55 in turn to promote the reactivation of PP2A-B56 by dephosphorylating a PP1-docking site in PP2A-B56, thereby promoting the recruitment of PP1. PP1 recruitment to human, mitotic PP2A-B56 holoenzymes and the sequences of these conserved PP1-docking motifs suggest that PP1 regulates PP2A-B55 and PP2A-B56 activities in a variety of signalling contexts throughout eukaryotes.
Figures


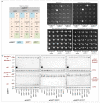








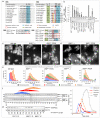


Comment in
-
Cell cycle: It takes three to find the exit.Nature. 2015 Jan 1;517(7532):29-30. doi: 10.1038/nature14080. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Nature. 2015. PMID: 25487157 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ohkura H, Kinoshita N, Miyatani S, Toda T, Yanagida M. The Fission Yeast dis2+ Gene Required For Chromosome Disjoining Encodes One Of 2 Putative Type-1 Protein Phosphatases. Cell. 1989;57:997–1007. - PubMed
-
- Mochida S, Hunt T. Calcineurin is required to release Xenopus egg extracts from meiotic M phase. Nature. 2007;449:336–340. doi:10.1038/nature06121. - PubMed
-
- Schmitz MH, Held M, Janssens V, Hutchins JR, Hudecz O, Ivanova E, Goris J, Trinkle-Mulcahy L, Lamond AI, Poser I, Hyman AA, Mechtler K, Peters JM, Gerlich DW. Live-cell imaging RNAi screen identifies PP2A-B55alpha and importin-beta1 as key mitotic exit regulators in human cells. Nature cell biology. 2010;12:886–893. doi:10.1038/ncb2092. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

