Genomic locus on chromosome 1 regulates susceptibility to spontaneous arthritis in mice deficiency of IL-1RA
- PMID: 25488730
- PMCID: PMC4272550
- DOI: 10.1186/s12865-014-0057-9
Genomic locus on chromosome 1 regulates susceptibility to spontaneous arthritis in mice deficiency of IL-1RA
Abstract
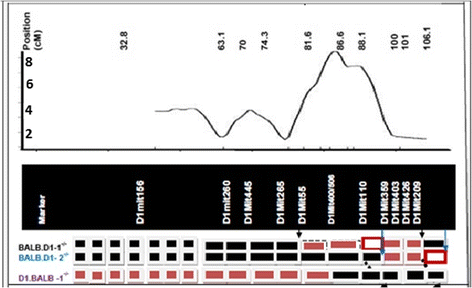
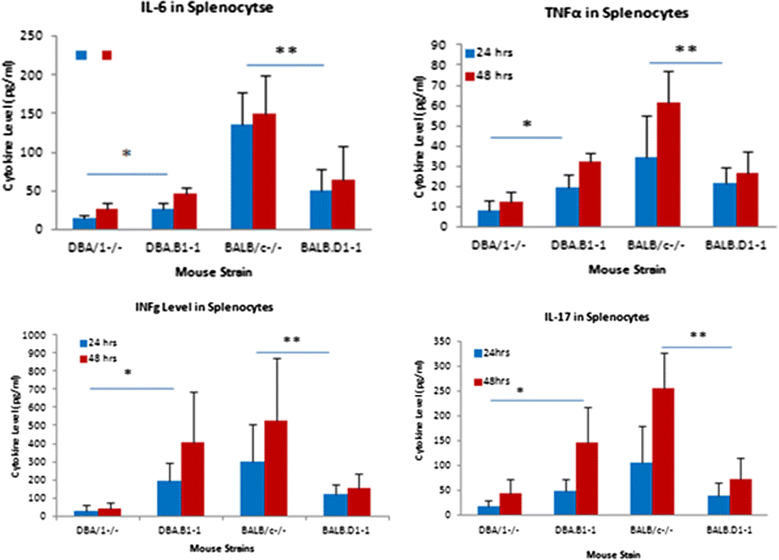
Background: To understand the role of genetic factors on chromosome 1 in the regulation of spontaneous arthritis in mice deficient in IL-1 receptor antagonist protein (IL_1RA), we previously used speed congenic breeding to transfer the QTL region from DBA/1(-/-) mice that are resistant to spontaneous arthritis into BALB/c(-/-) mice which are susceptible. We were able to establish two congenic strains which exhibited a delayed onset and reduced severity of disease. In this study, we asked a different set of questions. How will the QTL region from BALB/c(-/-) interact with the rest of the genome in the DBA/1(-/-) background? Will the DBA/1(-/-) mice become susceptible to spontaneous arthritis if the QTL genomic region on chromosome 1 was replaced with the genomic fragment of the same region from BALB/c(-/-)? We conducted the congenic breeding with the similar procedure as that of congenic strains with BALB/c(-/-) background.
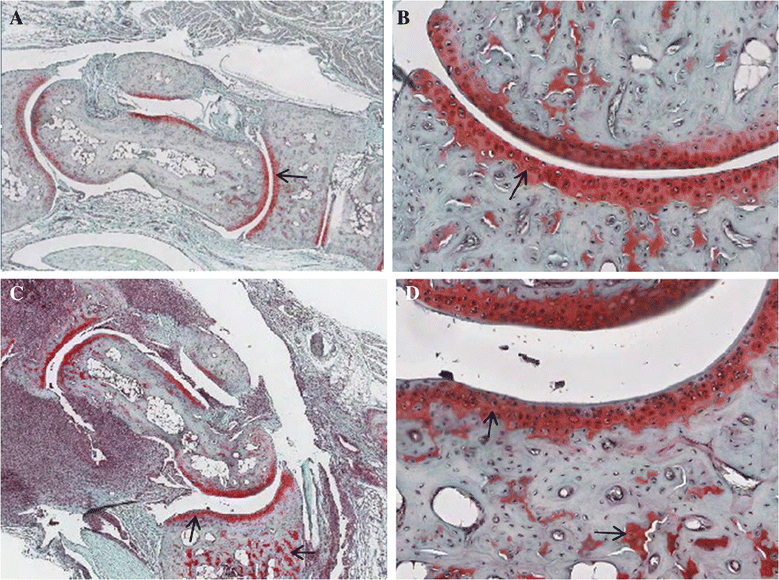
Result: Instead of BALB/c(-/-), DBA/1(-/-) was used as the recurrent parent while BALB/c(-/-) was used as the donor parent. By the 6(th) generation we determined that all of the chromosomes in the progeny were of DBA/1(-/-) origin with the exception of the QTL portion of chromosome 1 which is heterozygous of BALB/c(-/-) and DBA/1(-/-) origin. We then intercrossed selected mice to produce homozygous strains containing the homozygous genomic region of BALB/c(-/-) on chromosome 1, while the rest of genome are homozygous DBA/1(-/-). This strain was observed for the development of spontaneous arthritis. Up to 9 weeks of age, both congenic strain and DBA/1(-/-) did not develop arthritis. However, after 9 weeks, the congenic strain started to exhibit signs of arthritis, while the DBA/1(-/-) remained free from disease.
Conclusion: The result indicates a strong influence of genetic factor(s) on the QTL of chromosome 1 on the susceptibility to spontaneous arthritis. Identification of genetic factors within this QTL region in the future will significantly enhance our understanding of molecular mechanism of spontaneous arthritis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Congenic mice provide evidence for a genetic locus that modulates spontaneous arthritis caused by deficiency of IL-1RA.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 28;8(6):e68158. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068158. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23840826 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased expression levels of Ifi genes is associated to the increased resistance to spontaneous arthritis disease in mice deficiency of IL-1RA.BMC Immunol. 2016 Aug 2;17(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12865-016-0163-y. BMC Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27480124 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying a major locus that regulates spontaneous arthritis in IL-1ra-deficient mice and analysis of potential candidates.Genet Res (Camb). 2011 Apr;93(2):95-103. doi: 10.1017/S0016672310000704. Epub 2011 Mar 18. Genet Res (Camb). 2011. PMID: 21414240 Free PMC article.
-
Arthritis in mice that are deficient in interleukin-1 receptor antagonist is dependent on genetic background.Arthritis Rheum. 2005 Dec;52(12):3731-8. doi: 10.1002/art.21481. Arthritis Rheum. 2005. PMID: 16320323
-
The complexity in hunting for candidate genes within QTL that determine susceptibility to arthritis in rats.Crit Rev Immunol. 2008;28(2):127-57. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v28.i2.30. Crit Rev Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18540828 Review.
Cited by
-
Deficiency of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in mice differentially affects bone properties under different genomic backgrounds.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 27;14(1):19889. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70454-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39191800 Free PMC article.
-
Variation of sexual dimorphism and asymmetry in disease expression of inflammatory arthritis among laboratory mouse models with different genomic backgrounds.Lab Anim Res. 2023 Dec 20;39(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s42826-023-00185-0. Lab Anim Res. 2023. PMID: 38115139 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Koenders MI, Devesa I, Marijnissen RJ, Abdollahi-Roodsaz S, Boots AMH, Walgreen B, di Padova FE, Nicklin MJH, Joosten LAB, van den Berg WB. Interleukin-1 drives pathogenic Th17. Cells during spontaneous arthritis in interleukin-1 receptor antagonist–deficient mice. Arthiritis Rheum. 2008;58:3461–3470. doi: 10.1002/art.23957. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Horai R, Nakajima A, Habiro K, Kotani M, Nakae S, Matsuki T, Nambu A, Saijo S, Kotaki H, Sudo K, Okahara A, Tanioka H, Ikuse T, Ishii N, Schwartzberg PL, Abe R, Iwakura Y. TNFα is crucial for the development of autoimmune arthritis in IL-1 receptor antagonist-deficient mice. J Clin Invest. 2004;114:1603–1611. doi: 10.1172/JCI20742. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

