The histone demethylase enzyme KDM3A is a key estrogen receptor regulator in breast cancer
- PMID: 25488809
- PMCID: PMC4288188
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku1298
The histone demethylase enzyme KDM3A is a key estrogen receptor regulator in breast cancer
Abstract
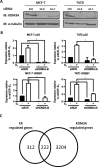
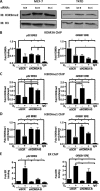
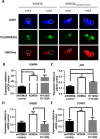
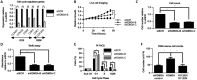
Endocrine therapy has successfully been used to treat estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer, but this invariably fails with cancers becoming refractory to treatment. Emerging evidence has suggested that fluctuations in ER co-regulatory protein expression may facilitate resistance to therapy and be involved in breast cancer progression. To date, a small number of enzymes that control methylation status of histones have been identified as co-regulators of ER signalling. We have identified the histone H3 lysine 9 mono- and di-methyl demethylase enzyme KDM3A as a positive regulator of ER activity. Here, we demonstrate that depletion of KDM3A by RNAi abrogates the recruitment of the ER to cis-regulatory elements within target gene promoters, thereby inhibiting estrogen-induced gene expression changes. Global gene expression analysis of KDM3A-depleted cells identified gene clusters associated with cell growth. Consistent with this, we show that knockdown of KDM3A reduces ER-positive cell proliferation and demonstrate that KDM3A is required for growth in a model of endocrine therapy-resistant disease. Crucially, we show that KDM3A catalytic activity is required for both ER-target gene expression and cell growth, demonstrating that developing compounds which target demethylase enzymatic activity may be efficacious in treating both ER-positive and endocrine therapy-resistant disease.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lysine demethylase KDM3A regulates breast cancer cell invasion and apoptosis by targeting histone and the non-histone protein p53.Oncogene. 2017 Jan 5;36(1):47-59. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.174. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 27270439 Free PMC article.
-
KDM4B is a master regulator of the estrogen receptor signalling cascade.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Aug;41(14):6892-904. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt469. Epub 2013 May 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23723241 Free PMC article.
-
The Histone Demethylase Enzymes KDM3A and KDM4B Co-Operatively Regulate Chromatin Transactions of the Estrogen Receptor in Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Aug 6;11(8):1122. doi: 10.3390/cancers11081122. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31390833 Free PMC article.
-
The crucial role of epigenetic regulation in breast cancer anti-estrogen resistance: Current findings and future perspectives.Semin Cancer Biol. 2022 Jul;82:35-59. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.12.004. Epub 2020 Dec 7. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022. PMID: 33301860 Review.
-
Hypoxia and Hormone-Mediated Pathways Converge at the Histone Demethylase KDM4B in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 13;19(1):240. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010240. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29342868 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Histone demethylase Jumonji domain-containing 1A inhibits proliferation and progression of gastric cancer by upregulating runt-related transcription factor 3.Cancer Sci. 2020 Oct;111(10):3679-3692. doi: 10.1111/cas.14594. Epub 2020 Sep 6. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 32762126 Free PMC article.
-
Crucial Functions of the JMJD1/KDM3 Epigenetic Regulators in Cancer.Mol Cancer Res. 2021 Jan;19(1):3-13. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-0404. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Mol Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 32605929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Histone Demethylase KDM3A, Increased in Human Pancreatic Tumors, Regulates Expression of DCLK1 and Promotes Tumorigenesis in Mice.Gastroenterology. 2019 Dec;157(6):1646-1659.e11. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.08.018. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 31442435 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Demethylase KDM3 (JMJD1) in Transcriptional Regulation and Cancer Progression.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1433:69-86. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-38176-8_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37751136 Free PMC article.
-
JMJD1A promotes tumorigenesis and forms a feedback loop with EZH2/let-7c in NSCLC cells.Tumour Biol. 2016 Aug;37(8):11237-47. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-4999-9. Epub 2016 Mar 5. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26945572
References
-
- Howard J.H., Bland K.I. Current management and treatment strategies for breast cancer. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012;24:44–48. - PubMed
-
- Johnston S.R., Saccani-Jotti G., Smith I.E., Salter J., Newby J., Coppen M., Ebbs S.R., Dowsett M. Changes in estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and pS2 expression in tamoxifen-resistant human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1995;55:3331–3338. - PubMed
-
- Green K.A., Carroll J.S. Oestrogen-receptor-mediated transcription and the influence of co-factors and chromatin state. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2007;7:713–722. - PubMed
-
- Lupien M., Brown M. Cistromics of hormone-dependent cancer. Endocr. Cancer. 2009;16:381–389. - PubMed
-
- Anzick S.L., Kononen J., Walker R.L., Azorsa D.O., Tanner M.M., Guan X.Y., Sauter G., Kallioniemi O.P., Trent J.M., Meltzer P.S. AIB1, a steroid receptor coactivator amplified in breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1997;277:965–968. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

