The histone demethylase enzyme KDM3A is a key estrogen receptor regulator in breast cancer
- PMID: 25488809
- PMCID: PMC4288188
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku1298
The histone demethylase enzyme KDM3A is a key estrogen receptor regulator in breast cancer
Abstract
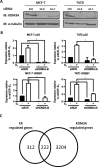
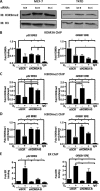
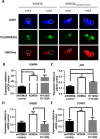
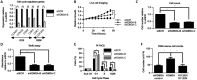
Endocrine therapy has successfully been used to treat estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer, but this invariably fails with cancers becoming refractory to treatment. Emerging evidence has suggested that fluctuations in ER co-regulatory protein expression may facilitate resistance to therapy and be involved in breast cancer progression. To date, a small number of enzymes that control methylation status of histones have been identified as co-regulators of ER signalling. We have identified the histone H3 lysine 9 mono- and di-methyl demethylase enzyme KDM3A as a positive regulator of ER activity. Here, we demonstrate that depletion of KDM3A by RNAi abrogates the recruitment of the ER to cis-regulatory elements within target gene promoters, thereby inhibiting estrogen-induced gene expression changes. Global gene expression analysis of KDM3A-depleted cells identified gene clusters associated with cell growth. Consistent with this, we show that knockdown of KDM3A reduces ER-positive cell proliferation and demonstrate that KDM3A is required for growth in a model of endocrine therapy-resistant disease. Crucially, we show that KDM3A catalytic activity is required for both ER-target gene expression and cell growth, demonstrating that developing compounds which target demethylase enzymatic activity may be efficacious in treating both ER-positive and endocrine therapy-resistant disease.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Howard J.H., Bland K.I. Current management and treatment strategies for breast cancer. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012;24:44–48. - PubMed
-
- Johnston S.R., Saccani-Jotti G., Smith I.E., Salter J., Newby J., Coppen M., Ebbs S.R., Dowsett M. Changes in estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and pS2 expression in tamoxifen-resistant human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1995;55:3331–3338. - PubMed
-
- Green K.A., Carroll J.S. Oestrogen-receptor-mediated transcription and the influence of co-factors and chromatin state. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2007;7:713–722. - PubMed
-
- Lupien M., Brown M. Cistromics of hormone-dependent cancer. Endocr. Cancer. 2009;16:381–389. - PubMed
-
- Anzick S.L., Kononen J., Walker R.L., Azorsa D.O., Tanner M.M., Guan X.Y., Sauter G., Kallioniemi O.P., Trent J.M., Meltzer P.S. AIB1, a steroid receptor coactivator amplified in breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1997;277:965–968. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

