A new heavy lanthanide-dependent DNAzyme displaying strong metal cooperativity and unrescuable phosphorothioate effect
- PMID: 25488814
- PMCID: PMC4288186
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku1296
A new heavy lanthanide-dependent DNAzyme displaying strong metal cooperativity and unrescuable phosphorothioate effect
Abstract
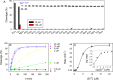
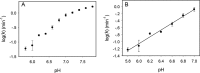
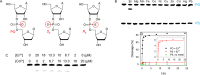
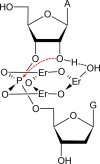
In vitro selection of RNA-cleaving DNAzymes was performed using three heavy lanthanide ions (Ln(3+)): Ho(3+), Er(3+) and Tm(3+). The resulting sequences were aligned together and about half of the library contained a new family of DNAzyme. These DNAzymes have a simple loop structure, and they are active only with the seven heavy Ln(3+). Among the tested non-lanthanide ions, only Y(3+) induced cleavage and even Pb(2+) failed to cleave, suggesting a very high specificity. A representative DNAzyme, Tm7, has a sigmoidal metal binding curve with a Hill coefficient of 3, indicating that three metal ions are involved in the catalytic step. Its pH-rate profile has a slope of 1, suggesting a single deprotonation step is involved in the rate-limiting step. Tm7 has a cleavage rate of 1.6 min(-1) at pH 7.8 with 10 μM Er(3+). Phosphorothioate substitution at the cleavage junction completely inhibits the activity, which cannot be rescued by Cd(2+) alone, or by a mixture of Er(3+) and Cd(2+), suggesting that two interacting metal ions are involved in direct bonding to both non-bridging oxygen atoms. A new model involving three lanthanide ions is proposed based on this study. A biosensor is engineered using Tm7 to detect Dy(3+) down to 14 nM.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


References
-
- Komiyama M., Takeda N., Shigekawa H. Hydrolysis of DNA and RNA by lanthanide ions: mechanistic studies leading to new applications. Chem. Commun. 1999:1443–1451.
-
- Kim H.-K., Li J., Nagraj N., Lu Y. Probing metal binding in the 8–17 DNAzyme by TbIII luminescence spectroscopy. Chem. Eur. J. 2008;14:8696–8703. - PubMed
-
- Feig A.L., Panek M., Horrocks W.D., Jr, Uhlenbeck O.C. Probing the binding of Tb(III) and Eu(III) to the hammerhead ribozyme using luminescence spectroscopy. Chem. Biol. 1999;6:801–810. - PubMed
-
- Marciniec T., Ciesiołka J., Wrzesinski J., Krzyżosiak W.J. Identification of the magnesium, europium and lead binding sites in E. Coli and lupine tRNAphe by specific metal ion-induced cleavages. FEBS Lett. 1989;243:293–298. - PubMed
-
- Komiyama M., Sumaoka J. Progress towards synthetic enzymes for phosphoester hydrolysis. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1998;2:751–757. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

