Gain-of-function CCR4 mutations in adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma
- PMID: 25488980
- PMCID: PMC4267233
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20140987
Gain-of-function CCR4 mutations in adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma
Abstract
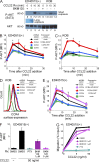
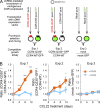
Adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL) is an aggressive malignancy caused by human T cell lymphotropic virus type-I (HTLV-I) without curative treatment at present. To illuminate the pathogenesis of ATLL we performed whole transcriptome sequencing of purified ATLL patient samples and discovered recurrent somatic mutations in CCR4, encoding CC chemokine receptor 4. CCR4 mutations were detected in 14/53 ATLL samples (26%) and consisted exclusively of nonsense or frameshift mutations that truncated the coding region at C329, Q330, or Y331 in the carboxy terminus. Functionally, the CCR4-Q330 nonsense isoform was gain-of-function because it increased cell migration toward the CCR4 ligands CCL17 and CCL22, in part by impairing receptor internalization. This mutant enhanced PI(3) kinase/AKT activation after receptor engagement by CCL22 in ATLL cells and conferred a growth advantage in long-term in vitro cultures. These findings implicate somatic gain-of-function CCR4 mutations in the pathogenesis of ATLL and suggest that inhibition of CCR4 signaling might have therapeutic potential in this refractory malignancy.
Figures


Comment in
-
CCR4 drives ATLL jail break.J Exp Med. 2014 Dec 15;211(13):2485. doi: 10.1084/jem.21113insight5. J Exp Med. 2014. PMID: 25512583 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Arisawa K., Soda M., Endo S., Kurokawa K., Katamine S., Shimokawa I., Koba T., Takahashi T., Saito H., Doi H., and Shirahama S.. 2000. Evaluation of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma incidence and its impact on non-Hodgkin lymphoma incidence in southwestern Japan. Int. J. Cancer. 85:319–324 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(20000201)85:3<319::AID-IJC4>3.0.CO;2-B - DOI - PubMed
-
- Balabanian K., Lagane B., Pablos J.L., Laurent L., Planchenault T., Verola O., Lebbe C., Kerob D., Dupuy A., Hermine O., et al. 2005. WHIM syndromes with different genetic anomalies are accounted for by impaired CXCR4 desensitization to CXCL12. Blood. 105:2449–2457 10.1182/blood-2004-06-2289 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cao Y., Hunter Z.R., Liu X., Xu L., Yang G., Chen J., Patterson C.J., Tsakmaklis N., Kanan S., Rodig S., et al. 2014. The WHIM-like CXCR4S338X somatic mutation activates AKT and ERK, and promotes resistance to ibrutinib and other agents used in the treatment of Waldenstrom’s Macroglobulinemia. Leukemia. In press. 10.1038/leu.2014.187 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

