Structure-activity relationships of imidazole-derived 2-[N-carbamoylmethyl-alkylamino]acetic acids, dual binders of human insulin-degrading enzyme
- PMID: 25489670
- PMCID: PMC4325277
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.12.005
Structure-activity relationships of imidazole-derived 2-[N-carbamoylmethyl-alkylamino]acetic acids, dual binders of human insulin-degrading enzyme
Abstract
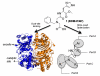
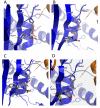
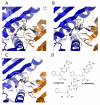
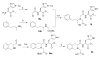
Insulin degrading enzyme (IDE) is a zinc metalloprotease that degrades small amyloid peptides such as amyloid-â and insulin. So far the dearth of IDE-specific pharmacological inhibitors impacts the understanding of its role in the physiopathology of Alzheimer's disease, amyloid-â clearance, and its validation as a potential therapeutic target. Hit 1 was previously discovered by high-throughput screening. Here we describe the structure-activity study, that required the synthesis of 48 analogues. We found that while the carboxylic acid, the imidazole and the tertiary amine were critical for activity, the methyl ester was successfully optimized to an amide or a 1,2,4-oxadiazole. Along with improving their activity, compounds were optimized for solubility, lipophilicity and stability in plasma and microsomes. The docking or co-crystallization of some compounds at the exosite or the catalytic site of IDE provided the structural basis for IDE inhibition. The pharmacokinetic properties of best compounds 44 and 46 were measured in vivo. As a result, 44 (BDM43079) and its methyl ester precursor 48 (BDM43124) are useful chemical probes for the exploration of IDE's role.
Keywords: Amyloid-beta peptides; Docking; Enzymes; Inhibitors; Structure–activity relationships; X-ray diffraction.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures
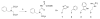



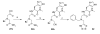

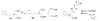
References
-
- Fernandez-Gamba A, Leal MC, Morelli L, Castano EM. Insulin-degrading enzyme: structure-function relationship and its possible roles in health and disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009;15:3644–3655. - PubMed
-
- Roth RA, Mesirow ML, Yokono K, Baba S. Degradation of insulin-like growth factors I and II by a human insulin degrading enzyme. Endocr. Res. 1984;10:101–112. - PubMed
- Guo Q, Manolopoulou M, Bian Y, Schilling AB, Tang W-J. Molecular Basis for the Recognition and Cleavages of IGF-II, TGF-[alpha], and Amylin by Human Insulin-Degrading Enzyme. J. Mol. Biol. 2010;395:430–443. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ciaccio C, Tundo GR, Grasso G, Spoto G, Marasco D, Ruvo M, Gioia M, Rizzarelli E, Coletta M. Somatostatin: A Novel Substrate and a Modulator of Insulin-Degrading Enzyme Activity. J. Mol. Biol. 2009;385:1556–1567. - PubMed
- Ralat LA, Guo Q, Ren M, Funke T, Dickey DM, Potter LR, Tang W-J. Insulin-degrading enzyme modulates the natriuretic peptide-mediated signaling response. J. Biol. Chem. 2011;286:4670–4679. - PMC - PubMed
- Ren M, Guo Q, Guo L, Lenz M, Qian F, Koenen RR, Xu H, Schilling AB, Weber C, Ye RD, Dinner AR, Tang W-J. Polymerization of MIP-1 chemokine (CCL3 and CCL4) and clearance of MIP-1 by insulin-degrading enzyme. EMBO J. 2010;29:3952–3966. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kurochkin IV, Goto S. Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid peptide specifically interacts with and is degraded by insulin degrading enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1994;345:33–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

