Plasma lipoprotein(a) levels are associated with mild renal impairment in type 2 diabetics independent of albuminuria
- PMID: 25490096
- PMCID: PMC4260843
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114397
Plasma lipoprotein(a) levels are associated with mild renal impairment in type 2 diabetics independent of albuminuria
Abstract
Background: CKD, an independent risk factor for CV disease, increases mortality in T2DM. Treating modifiable CV risk factors decreases mortality in diabetics with microalbuminuria, but the role of early CV prevention in diabetics with mild CKD by GFR criteria alone remains unclear. The purpose of this study was to probe whether T2DM patients with mild GFR impairment have atherogenic lipid profiles compared to diabetic counterparts with normal renal function.
Methods: In the Penn Diabetes Heart Study (PDHS), a single-center observational cohort of T2DM patients without clinical CVD, cross-sectional analyses were performed for directly measured lipid fractions in 1852 subjects with eGFR>60 mL/min/1.73 m² determined by the CKD-EPI equation (n = 1852). Unadjusted and multivariable analyses of eGFR association with log-transformed lipid parameters in incremental linear and logistic regression models (with eGFR 90 mL/min/1.73 m² as a cut-point) were performed.
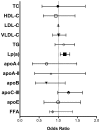
Results: Mild GFR impairment (eGFR 60-90 mL/min/1.73 m², median urinary ACR 5.25 mg/g) was associated with higher log-transformed Lp(a) values (OR 1.17, p = 0.005) and with clinically atherogenic Lp(a) levels above 30 mg/dL (OR 1.35, p = 0.013) even after full adjustment for demographics, medications, metabolic parameters, and albuminuria. Logistic regression demonstrated a trend towards significance between worse kidney function and apoB (p = 0.17) as well as apoC-III (p = 0.067) in the fully adjusted model.
Conclusions: Elevated Lp(a) levels have a robust association with mild GFR impairment in type 2 diabetics independent of race, insulin resistance, and albuminuria.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relation of atherogenic lipoproteins with estimated glomerular filtration rate decline: a longitudinal study.BMC Nephrol. 2015 Aug 4;16:130. doi: 10.1186/s12882-015-0122-5. BMC Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 26238454 Free PMC article.
-
Non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol is associated more closely with albuminuria in Chinese type 2 diabetic patients with normal renal function, compared with traditional lipid parameters.J Clin Lipidol. 2012 Jul-Aug;6(4):382-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2012.01.008. Epub 2012 Jan 28. J Clin Lipidol. 2012. PMID: 22836076
-
Association between lipoprotein(a) and insulin-like growth factor I during puberty and the relationship to microalbuminuria in children and adolescents with IDDM.Diabetes Care. 1995 Jul;18(7):933-9. doi: 10.2337/diacare.18.7.933. Diabetes Care. 1995. PMID: 7555552
-
Subclinical Kidney Damage in Hypertensive Patients: A Renal Window Opened on the Cardiovascular System. Focus on Microalbuminuria.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;956:279-306. doi: 10.1007/5584_2016_85. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 27873229 Review.
-
The impacts of albuminuria and low eGFR on the risk of cardiovascular death, all-cause mortality, and renal events in diabetic patients: meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 30;8(8):e71810. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071810. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24147148 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association between serum lipoprotein(a) and mildly reduced eGFR: a cross-sectional study.BMC Nephrol. 2023 Dec 8;24(1):364. doi: 10.1186/s12882-023-03417-6. BMC Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 38066475 Free PMC article.
-
Serum lipoprotein (a) associates with a higher risk of reduced renal function: a prospective investigation.J Lipid Res. 2020 Oct;61(10):1320-1327. doi: 10.1194/jlr.RA120000771. Epub 2020 Jul 23. J Lipid Res. 2020. PMID: 32703886 Free PMC article.
-
Repeat Measures of Lipoprotein(a) Molar Concentration and Cardiovascular Risk.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 Feb 22;79(7):617-628. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.11.055. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35177190 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between different levels and patterns of dyslipidemia and glomerular filtration rate in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional survey of a regional cohort.J Clin Lab Anal. 2023 Jul;37(13-14):e24954. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24954. Epub 2023 Aug 3. J Clin Lab Anal. 2023. PMID: 37537785 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoprotein (a): impact by ethnicity and environmental and medical conditions.J Lipid Res. 2016 Jul;57(7):1111-25. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R051904. Epub 2015 Dec 4. J Lipid Res. 2016. PMID: 26637279 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sarnak MJ (2003) Kidney Disease as a Risk Factor for Development of Cardiovascular Disease: A Statement From the American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention. Circulation 108:2154–2169 10.1161/01.CIR.0000095676.90936.80. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Manjunath G, Tighiouart H, Ibrahim H, MacLeod B, Salem DN, et al. (2003) Level of kidney function as a risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular outcomes in the community. J Am Coll Cardiol 41:47–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

