RNA virus attenuation by codon pair deoptimisation is an artefact of increases in CpG/UpA dinucleotide frequencies
- PMID: 25490153
- PMCID: PMC4383024
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.04531
RNA virus attenuation by codon pair deoptimisation is an artefact of increases in CpG/UpA dinucleotide frequencies
Abstract
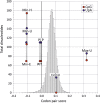
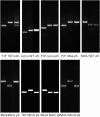
Mutating RNA virus genomes to alter codon pair (CP) frequencies and reduce translation efficiency has been advocated as a method to generate safe, attenuated virus vaccines. However, selection for disfavoured CPs leads to unintended increases in CpG and UpA dinucleotide frequencies that also attenuate replication. We designed and phenotypically characterised mutants of the picornavirus, echovirus 7, in which these parameters were independently varied to determine which most influenced virus replication. CpG and UpA dinucleotide frequencies primarily influenced virus replication ability while no fitness differences were observed between mutants with different CP usage where dinucleotide frequencies were kept constant. Contrastingly, translation efficiency was unaffected by either CP usage or dinucleotide frequencies. This mechanistic insight is critical for future rational design of live virus vaccines and their safety evaluation; attenuation is mediated through enhanced innate immune responses to viruses with elevated CpG/UpA dinucleotide frequencies rather the viruses themselves being intrinsically defective.
Keywords: CpG; E. coli; arabidopsis; codon pair bias; dinucleotide; echovirus 7; evolutionary biology; genomics; human; infectious disease; microbiology; picornavirus; vaccine; viruses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
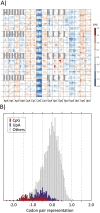
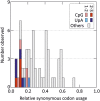



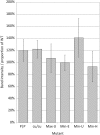
References
-
- Atkinson NJ, Witteveldt J, Evans DJ, Simmonds P. The Influence of CpG and UpA dinucleotide frequencies on RNA virus replication and characterisation of the innate cellular pathways underlying virus attenuation and enhanced replication. Nucleic Acids Research. 2014;42:4527–4545. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku075. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bennetzen JL, Hall BD. Codon selection in yeast. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1982;257:3026–3031. - PubMed
-
- Beutler E, Gelbart T, Han JH, Koziol JA, Beutler B. Evolution of the genome and the genetic code: selection at the dinucleotide level by methylation and polyribonucleotide cleavage. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of USA. 1989;86:192–196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.192. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- C20035/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0901002/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT087628MA/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BB/L004526/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- 095831/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

