Interferon gamma signaling positively regulates hematopoietic stem cell emergence
- PMID: 25490269
- PMCID: PMC4371141
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.11.007
Interferon gamma signaling positively regulates hematopoietic stem cell emergence
Abstract
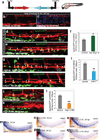
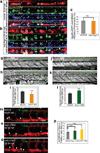
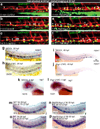
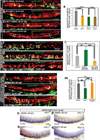
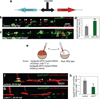
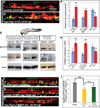
Vertebrate hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) emerge in the aorta-gonad-mesonephros (AGM) region from "hemogenic" endothelium. Here we show that the proinflammatory cytokine interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and its receptor Crfb17 positively regulate HSC development in zebrafish. This regulation does not appear to modulate the proliferation or survival of HSCs or endothelial cells, but rather the endothelial-to-HSC transition. Notch signaling and blood flow positively regulate the expression of ifng and crfb17 in the AGM. Notably, IFN-γ overexpression partially rescues the HSC loss observed in the absence of blood flow or Notch signaling. Importantly, IFN-γ signaling acts cell autonomously to control the endothelial-to-HSC transition. IFN-γ activates Stat3, an atypical transducer of IFN-γ signaling, in the AGM, and Stat3 inhibition decreases HSC formation. Together, our findings uncover a developmental role for an inflammatory cytokine and place its action downstream of Notch signaling and blood flow to control Stat3 activation and HSC emergence.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Aggad D, Stein C, Sieger D, Mazel M, Boudinot P, Herbomel P, Levraud JP, Lutfalla G, Leptin M. In vivo analysis of Ifn-gamma1 and Ifn-gamma2 signaling in zebrafish. J Immunol. 2010;185:6774–6782. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

