Impact of replacing smear microscopy with Xpert MTB/RIF for diagnosing tuberculosis in Brazil: a stepped-wedge cluster-randomized trial
- PMID: 25490549
- PMCID: PMC4260794
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001766
Impact of replacing smear microscopy with Xpert MTB/RIF for diagnosing tuberculosis in Brazil: a stepped-wedge cluster-randomized trial
Erratum in
-
Correction: Impact of Replacing Smear Microscopy with Xpert MTB/RIF for Diagnosing Tuberculosis in Brazil: A Stepped-Wedge Cluster-Randomized Trial.PLoS Med. 2015 Dec 3;12(12):e1001928. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001928. eCollection 2015 Dec. PLoS Med. 2015. PMID: 26632815 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Abundant evidence on Xpert MTB/RIF accuracy for diagnosing tuberculosis (TB) and rifampicin resistance has been produced, yet there are few data on the population benefit of its programmatic use. We assessed whether the implementation of Xpert MTB/RIF in routine conditions would (1) increase the notification rate of laboratory-confirmed pulmonary TB to the national notification system and (2) reduce the time to TB treatment initiation (primary endpoints).
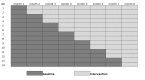
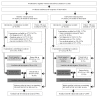
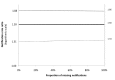
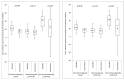
Methods and findings: We conducted a stepped-wedge cluster-randomized trial from 4 February to 4 October 2012 in 14 primary care laboratories in two Brazilian cities. Diagnostic specimens were included for 11,705 baseline (smear microscopy) and 12,522 intervention (Xpert MTB/RIF) patients presumed to have TB. Single-sputum-sample Xpert MTB/RIF replaced two-sputum-sample smear microscopy for routine diagnosis of pulmonary TB. In total, 1,137 (9.7%) tests in the baseline arm and 1,777 (14.2%) in the intervention arm were positive (p<0.001), resulting in an increased bacteriologically confirmed notification rate of 59% (95% CI = 31%, 88%). However, the overall notification rate did not increase (15%, 95% CI = -6%, 37%), and we observed no change in the notification rate for those without a test result (-3%, 95% CI = -37%, 30%). Median time to treatment decreased from 11.4 d (interquartile range [IQR] = 8.5-14.5) to 8.1 d (IQR = 5.4-9.3) (p = 0.04), although not among confirmed cases (median 7.5 [IQR = 4.9-10.0] versus 7.3 [IQR = 3.4-9.0], p = 0.51). Prevalence of rifampicin resistance detected by Xpert was 3.3% (95% CI = 2.4%, 4.3%) among new patients and 7.4% (95% CI = 4.3%, 11.7%) among retreatment patients, with a 98% (95% CI = 87%, 99%) positive predictive value compared to phenotypic drug susceptibility testing. Missing data in the information systems may have biased our primary endpoints. However, sensitivity analyses assessing the effects of missing data did not affect our results.
Conclusions: Replacing smear microscopy with Xpert MTB/RIF in Brazil increased confirmation of pulmonary TB. An additional benefit was the accurate detection of rifampicin resistance. However, no increase on overall notification rates was observed, possibly because of high rates of empirical TB treatment.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01363765. Please see later in the article for the Editors' Summary.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Boehme CC, Nicol MP, Nabeta P, Michael JS, Gotuzzo E, et al. (2011) Feasibility, diagnostic accuracy, and effectiveness of decentralised use of the Xpert MTB/RIF test for diagnosis of tuberculosis and multidrug resistance: a multicentre implementation study. Lancet 377: 1495–1505 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60438-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Theron G, Zijenah L, Chanda D, Clowes P, Rachow A, et al. (2014) Feasibility, accuracy, and clinical effect of point-of-care Xpert MTB/RIF testing for tuberculosis in primary-care settings in Africa: a multicentre, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 383: 424–435 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62073-5 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

