MR fingerprinting using fast imaging with steady state precession (FISP) with spiral readout
- PMID: 25491018
- PMCID: PMC4461545
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.25559
MR fingerprinting using fast imaging with steady state precession (FISP) with spiral readout
Abstract
Purpose: This study explores the possibility of using gradient echo-based sequences other than balanced steady-state free precession (bSSFP) in the magnetic resonance fingerprinting (MRF) framework to quantify the relaxation parameters .
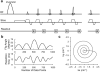
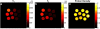
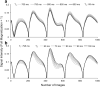
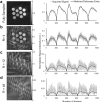
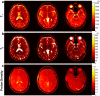
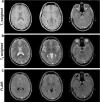
Methods: An MRF method based on a fast imaging with steady-state precession (FISP) sequence structure is presented. A dictionary containing possible signal evolutions with physiological range of T1 and T2 was created using the extended phase graph formalism according to the acquisition parameters. The proposed method was evaluated in a phantom and a human brain. T1 , T2 , and proton density were quantified directly from the undersampled data by the pattern recognition algorithm.
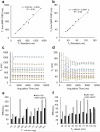
Results: T1 and T2 values from the phantom demonstrate that the results of MRF FISP are in good agreement with the traditional gold-standard methods. T1 and T2 values in brain are within the range of previously reported values.
Conclusion: MRF-FISP enables a fast and accurate quantification of the relaxation parameters. It is immune to the banding artifact of bSSFP due to B0 inhomogeneities, which could improve the ability to use MRF for applications beyond brain imaging.
Keywords: FISP; MR fingerprinting; quantitative imaging; relaxation time; spiral.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

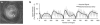
References
-
- Cheng H-LM, Stikov N, Ghugre NR, Wright GA. Practical medical applications of quantitative MR relaxometry. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 2012;36:805–24. - PubMed
-
- Look DC. Time Saving in Measurement of NMR and EPR Relaxation Times. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1970;41:250.
-
- Deoni SCL, Rutt BK, Peters TM. Rapid combined T1 and T2 mapping using gradient recalled acquisition in the steady state. Magn. Reson. Med. 2003;49:515–26. - PubMed
-
- Messroghli DR, Radjenovic A, Kozerke S, Higgins DM, Sivananthan MU, Ridgway JP. Modified Look-Locker inversion recovery (MOLLI) for high-resolution T1 mapping of the heart. Magn. Reson. Med. 2004;52:141–6. - PubMed
-
- Zhu DC, Penn RD. Full-brain T1 mapping through inversion recovery fast spin echo imaging with time-efficient slice ordering. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005;54:725–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

