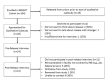
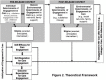
Multilevel challenges to engagement in HIV care after prison release: a theory-informed qualitative study comparing prisoners' perspectives before and after community reentry
- PMID: 25491946
- PMCID: PMC4295310
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-1253
Multilevel challenges to engagement in HIV care after prison release: a theory-informed qualitative study comparing prisoners' perspectives before and after community reentry
Abstract
Background: Although prison provides the opportunity for HIV diagnosis and access to in-prison care, following release, many HIV-infected inmates experience clinical setbacks, including nonadherence to antiretrovirals, elevations in viral load, and HIV disease progression. HIV-infected former inmates face numerous barriers to successful community reentry and to accessing healthcare. However, little is known about the outcome expectations of HIV-infected inmates for release, how their post-release lives align with pre-release expectations, and how these processes influence engagement in HIV care following release from prison.
Methods: We conducted semi-structured interviews (24 pre- and 13 post-release) with HIV-infected inmates enrolled in a randomized controlled trial of a case management intervention to enhance post-release linkage to care. Two researchers independently coded data using a common codebook. Intercoder reliability was strong (kappa = 0.86). We analyzed data using Grounded Theory methodology and Applied Thematic Analysis. We collected and compared baseline sociodemographic and behavioral characteristics of all cohort participants who did and did not participate in the qualitative interviews using Fisher's Exact Tests for categorical measures and Wilcoxon rank-sum tests for continuous measures.
Results: Most participants were heterosexual, middle-aged, single, African American men and women with histories of substance use. Substudy participants were more likely to anticipate living with family/friends and needing income assistance post-release. Most were taking antiretrovirals prior to release and anticipated needing help securing health benefits and medications post-release. Before release, most participants felt confident they would be able to manage their HIV. However, upon release, many experienced intermittent or prolonged periods of antiretroviral nonadherence, largely due to substance use relapse or delays in care initiation. Substance use was precipitated by stressful life experiences, including stigma, and contact with drug-using social networks. As informed by the Social Cognitive Theory and HIV Stigma Framework, findings illustrate the reciprocal relationships among substance use, experiences of stigma, pre- and post-release environments, and skills needed to engage in HIV care.
Conclusion: These findings underscore the need for comprehensive evidence-based interventions to prepare inmates to transition from incarceration to freedom, particularly those that strengthen linkage to HIV care and focus on realities of reentry, including stigma, meeting basic needs, preventing substance abuse, and identifying community resources.
Figures
Similar articles
-
"You're in a world of chaos": experiences accessing HIV care and adhering to medications after incarceration.J Assoc Nurses AIDS Care. 2015 Sep-Oct;26(5):542-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jana.2015.06.001. Epub 2015 Jun 14. J Assoc Nurses AIDS Care. 2015. PMID: 26188413 Free PMC article.
-
Medicaid Enrollment among Prison Inmates in a Non-expansion State: Exploring Predisposing, Enabling, and Need Factors Related to Enrollment Pre-incarceration and Post-Release.J Urban Health. 2018 Aug;95(4):454-466. doi: 10.1007/s11524-018-0275-1. J Urban Health. 2018. PMID: 29934825 Free PMC article.
-
The role of primary health care services to better meet the needs of Aboriginal Australians transitioning from prison to the community.BMC Fam Pract. 2015 Jul 22;16:86. doi: 10.1186/s12875-015-0303-0. BMC Fam Pract. 2015. PMID: 26198338 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and meta-analyses on initiation, adherence and outcomes of antiretroviral therapy in incarcerated people.PLoS One. 2020 May 18;15(5):e0233355. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233355. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32421754 Free PMC article.
-
Women and barriers to harm reduction services: a literature review and initial findings from a qualitative study in Barcelona, Spain.Harm Reduct J. 2020 Oct 19;17(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s12954-020-00429-5. Harm Reduct J. 2020. PMID: 33076931 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Facilitators and Barriers to adherence to antiretroviral therapy among incarcerated people living with HIV in Iran: insights from a qualitative study.Harm Reduct J. 2025 Jan 8;22(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12954-024-01151-2. Harm Reduct J. 2025. PMID: 39773185 Free PMC article.
-
A Qualitative Examination of Stigma Among Formerly Incarcerated Adults Living With HIV.Sage Open. 2016 Jan-Mar;6(1):10.1177/2158244016629524. doi: 10.1177/2158244016629524. Epub 2016 Feb 7. Sage Open. 2016. PMID: 27182459 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-related stigma and uptake of antiretroviral treatment among incarcerated individuals living with HIV/AIDS in South African correctional settings: A mixed methods analysis.PLoS One. 2021 Jul 30;16(7):e0254975. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254975. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34329311 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lessons Learned from the Pathways to Community Health Study to Evaluate the Transition of Care from Jail to Community for Men with HIV.AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2021 Sep;35(9):360-369. doi: 10.1089/apc.2021.0060. Epub 2021 Aug 31. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2021. PMID: 34463134 Free PMC article.
-
Facilitators of HIV Medical Care Engagement Among Former Prisoners.AIDS Educ Prev. 2015 Dec;27(6):566-83. doi: 10.1521/aeap.2015.27.6.566. AIDS Educ Prev. 2015. PMID: 26595268 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maruschak LM. Bureau of Justice Statistics Bulletin. 2010. HIV in Prisons, 2007-08.
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2458/14/1253/prepub
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials