Morphological and molecular characterization of Karyolysus--a neglected but common parasite infecting some European lizards
- PMID: 25492802
- PMCID: PMC4298996
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-014-0555-x
Morphological and molecular characterization of Karyolysus--a neglected but common parasite infecting some European lizards
Abstract
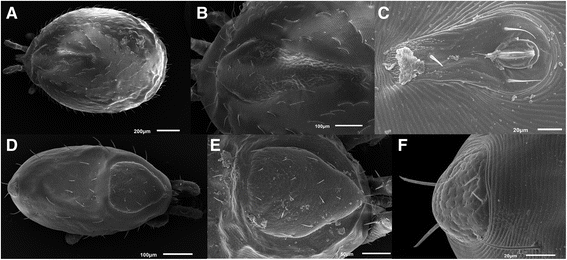
Background: Blood parasites of the genus Karyolysus Labbé, 1894 (Apicomplexa: Adeleida: Karyolysidae) represent the protozoan haemogregarines found in various genera of lizards, including Lacerta, Podarcis, Darevskia (Lacertidae) and Mabouia (Scincidae). The vectors of parasites are gamasid mites from the genus Ophionyssus.
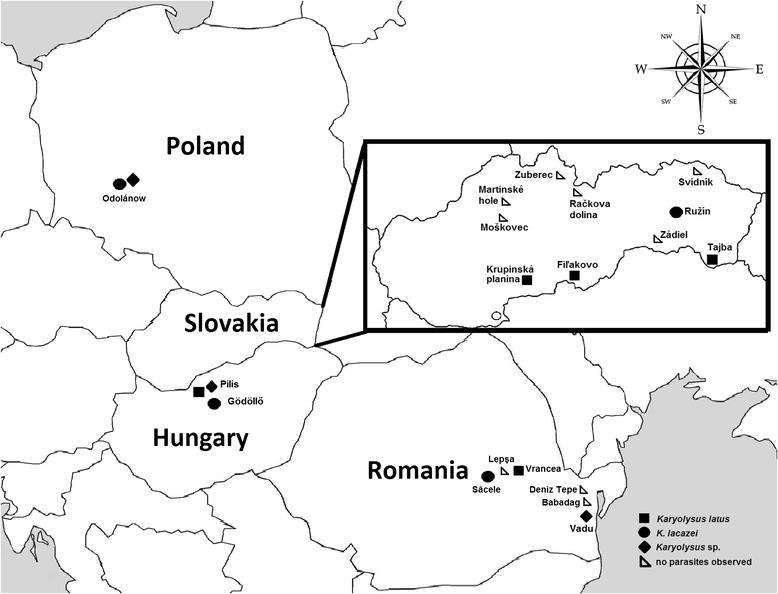
Methods: A total of 557 individuals of lacertid lizards were captured in four different localities in Europe (Hungary, Poland, Romania and Slovakia) and blood was collected. Samples were examined using both microscopic and molecular methods, and phylogenetic relationships of all isolates of Karyolysus sp. were assessed for the first time. Karyolysus sp. 18S rRNA isolates were evaluated using Bayesian and Maximum Likelihood analyses.
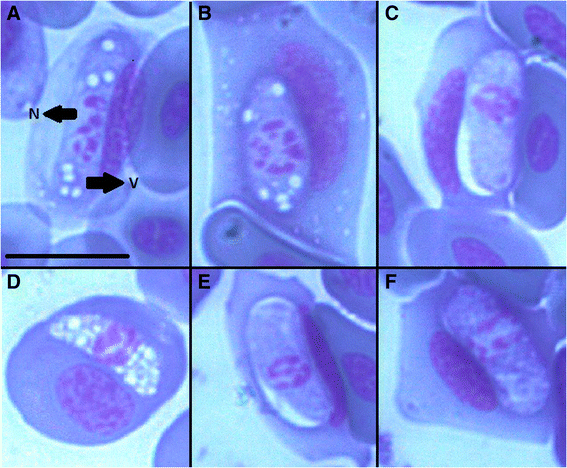
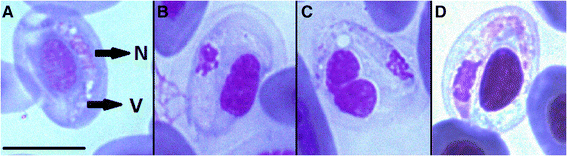
Results: A total of 520 blood smears were examined microscopically and unicellular protozoan parasites were found in 116 samples (22.3% prevalence). The presence of two Karyolysus species, K. latus and K. lacazei was identified. In total, of 210 samples tested by polymerase chain reaction (PCR), the presence of parasites was observed in 64 individuals (prevalence 30.5%). Results of phylogenetic analyses revealed the existence of four haplotypes, all part of the same lineage, with other parasites identified as belonging to the genus Hepatozoon.
Conclusions: Classification of these parasites using current taxonomy is complex - they were identified in both mites and ticks that typically are considered to host Karyolysus and Hepatozoon respectively. Furthermore although distortions to the intermediate host erythrocyte nuclei were observed, the defining characteristic of Karyolysus, the haplotypes were nearly identical to those reported from lizards in the Iberian Peninsula, where such distortions were not reported and which were thus identified as Hepatozoon. Based on the phylogenetic analyses, neither vertebrate host, nor geographical patterns of the studied blood parasites could be established.
Figures



References
-
- Telford SR. Hemoparasites of Reptilia, Color Atlas and Text. Boca Raton, Florida, USA: CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group; 2009.
-
- Hassl AR. Blood parasitism by hemogregarines in Central European lizards. Herpetozoa. 2012;25(1–2):83–86.
-
- Svahn K. Blood parasites of the genus Karyolysus (Coccidia, Adeleidae) in Scandinavian lizards. Description and life cycle. Norw J Zool. 1975;23:277–295.
-
- Svahn K. Incidence of blood parasites of the genus Karyolysus (Coccidia) in Scandinavian lizards. Oikos. 1974;25:43–53. doi: 10.2307/3543544. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

