The immunoglobulin heavy chain VH6-1 promoter regulates Ig transcription in non-B cells
- PMID: 25493072
- PMCID: PMC4260249
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-014-0114-8
The immunoglobulin heavy chain VH6-1 promoter regulates Ig transcription in non-B cells
Abstract
Background: Non-B cell immunoglobulins (Igs) are widely expressed in epithelial cancer cells. The past 20 years of research have demonstrated that non-B cell Igs are associated with cancer cell proliferation, the cellular cytoskeleton and cancer stem cells. In this study we explored the transcriptional mechanism of IgM production in non-B cells.
Methods: The promoter region of a V-segment of the heavy mu chain gene (VH6-1) was cloned from a colon cancer cell line HT-29. Next, the promoter activities in non-B cells and B-cells were detected using the dual-luciferase reporter assay. Then the transcription factor binding to the promoter regions was evaluated by electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSAs) and gel supershift experiments.
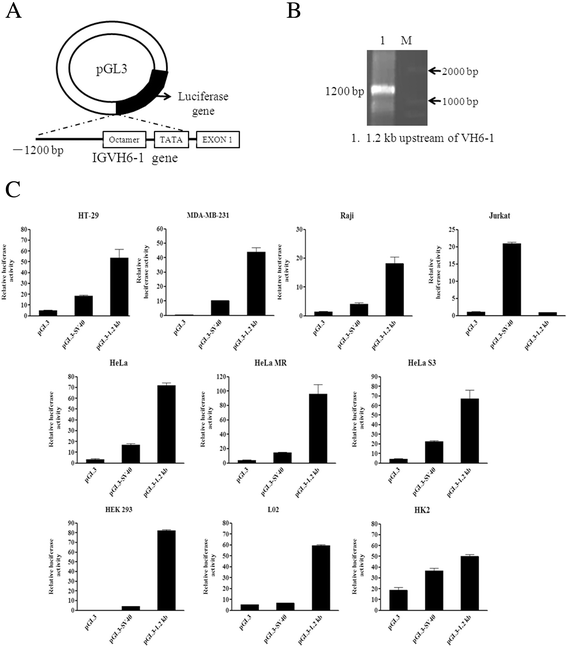
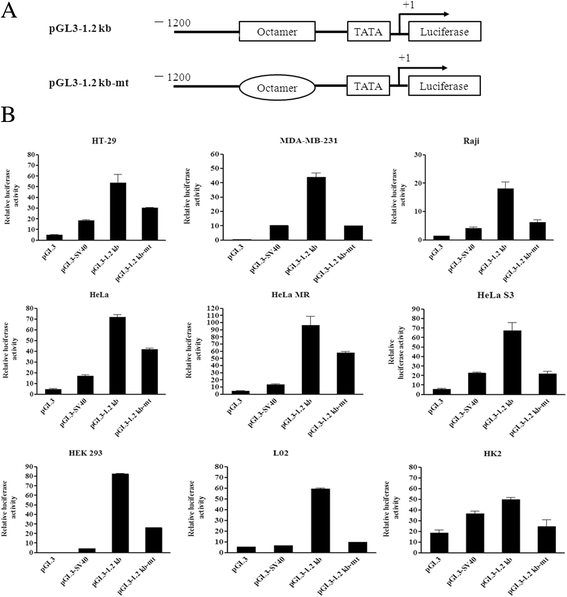
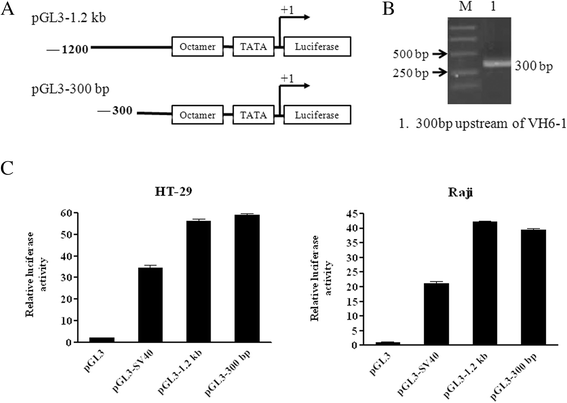
Results: Our data showed that the sequence 1200 bp upstream of VH6-1 exhibited promoter activity in both B and non-B cells. No new regulatory elements were identified within the region 1200 bp to 300 bp upstream of VH6-1. In addition, Oct-1 was found to bind to the octamer element of the Ig gene promoter in cancer cells, in contrast to B cells, which utilize the transcriptional factor Oct-2.
Conclusion: The regulatory mechanisms among different cell types controlling the production of IgM heavy chains are worth discussing.
Keywords: Non-B cells; Oct-1; Promoter activity; Transcriptional regulation; VH6-1.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Gene Rearrangement and Transcriptional Regulation of Non B Cell-Derived Immunoglobulin.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1445:47-57. doi: 10.1007/978-981-97-0511-5_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38967749 Review.
-
Analysis of the imperfect octamer-containing human immunoglobulin VH6 gene promoter.Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Mar 11;22(5):850-60. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.5.850. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994. PMID: 8139927 Free PMC article.
-
Bidirectional transcription from the human immunoglobulin VH6 gene promoter.Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Mar 11;22(5):861-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.5.861. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994. PMID: 7545916 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct regulatory mechanism of immunoglobulin gene transcription in epithelial cancer cells.Cell Mol Immunol. 2010 Jul;7(4):279-86. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2010.13. Epub 2010 May 17. Cell Mol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20473321 Free PMC article.
-
Expression pattern of the most JH-proximal human VH gene segment (VH6) in the B cell and antibody repertoire suggests a role of VH6-encoded IgM antibodies in early ontogeny.J Immunol. 1993 Jan 1;150(1):161-8. J Immunol. 1993. PMID: 8417121
Cited by
-
Immunoglobulin Expression in Cancer Cells and Its Critical Roles in Tumorigenesis.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 24;12:613530. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.613530. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33841396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Staphylococcal Protein A Induces Leukocyte Necrosis by Complexing with Human Immunoglobulins.mBio. 2021 Jun 29;12(3):e0089921. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00899-21. Epub 2021 Jun 1. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34060329 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of immunoglobulin G in human podocytes, and its role in cell viability and adhesion.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Jun;41(6):3296-3306. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3525. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29512722 Free PMC article.
-
The Gene Rearrangement and Transcriptional Regulation of Non B Cell-Derived Immunoglobulin.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1445:47-57. doi: 10.1007/978-981-97-0511-5_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38967749 Review.
-
IGK with conserved IGΚV/IGΚJ repertoire is expressed in acute myeloid leukemia and promotes leukemic cell migration.Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 17;6(36):39062-72. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5393. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26429876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Qiu X, Zhu X, Zhang L, Mao Y, Zhang J, Hao P, Li G, Lv P, Li Z, Sun X, Wu L, Zheng J, Deng Y, Hou C, Tang P, Zhang S, Zhang Y. Human epithelial cancers secrete immunoglobulin g with unidentified specificity to promote growth and survival of tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2003;63:6488–6495. - PubMed
-
- Liu H, Zheng H, Duan Z, Hu D, Li M, Liu S, Li Z, Deng X, Wang Z, Tang M, Shi Y, Yi W, Cao Y: LMP1-augmented kappa intron enhancer activity contributes to upregulation expression of Ig kappa light chain via NF-kappaB and AP-1 pathways in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.Mol Cancer 2009, 8:92. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

