The antioxidant and anti-cadmium toxicity properties of garlic extracts
- PMID: 25493198
- PMCID: PMC4256585
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.164
The antioxidant and anti-cadmium toxicity properties of garlic extracts
Abstract
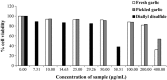
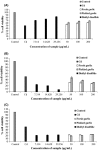
Cadmium (Cd) contamination is a highly dangerous international problem because it can transfer into the food chain and become bioaccumulated, endangering human health. Cd detoxication is very interesting particularly the method providing no undesirable side effects. Cd also causes lipid oxidation that leads to undesired food quality. Garlic (Allium sativum L.) has been used as conventional food and in herbal therapy and folklore medicine as an antibacterial, antitumorogenic, and antioxidant agent for over 5000 years. In the present work, fresh garlic and pickled garlic extracted with distilled water was brought to determine antioxidant activities in terms of 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging assay, 2,2'-azino-bis-3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulphonic acid (ABTS) radical scavenging assay, ferric reducing ability power (FRAP) assay, chelating activities, superoxide, and hydroxyl scavenging assay. The data showed that pickled garlic extracts significantly possessed more DPPH, ABTS, FRAP, superoxide, and hydroxyl scavenging assays as 11.86, 13.74, 4.9, 46.67, and 15.33 g trolox equivalent/g sample, respectively, compared with fresh one as 7.44, 7.62, 0.01, 4.07, and 8.09 g trolox equivalent/g sample, respectively. However, iron chelating activity of fresh garlic extract was higher than that of pickled garlic while there was no significant difference in the copper chelating activity of both extracts. For anti-Cd properties, pickled garlic was more effective than fresh garlic and contained less toxicity than standard diallyl disulfide (DADS). Therefore, therapeutic properties of pickled garlic favored its consumption compared with fresh and standard DADS for its antioxidant and anti-Cd properties.
Keywords: Anti-Cd; antioxidant; garlic; pickled garlic.
Figures
References
-
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry in USA. 2008. Case studies in environmental medicine (online). Available at http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/csem/ (accessed 11 January 2012)
-
- Amagase H. Clarifying the real bioactive constituents of garlic. J. Nutr. 2006;136:716S–725S. - PubMed
-
- AOAC (Association of official analytical chemists) Official methods of analysis of AOAC. 15th ed. Washington, DC: Allengton; 1990. (chapter 39)
-
- AOAC (Association of official analytical chemists) Official methods of analysis of AOAC. 16th ed. Washington, DC: Allengton; 1995. (chapter 39)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

