Small molecule substrate phosphorylation site inhibitors of protein kinases: approaches and challenges
- PMID: 25494294
- PMCID: PMC4301090
- DOI: 10.1021/cb5008376
Small molecule substrate phosphorylation site inhibitors of protein kinases: approaches and challenges
Abstract
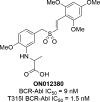
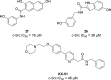
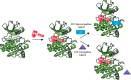
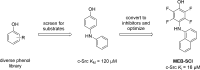
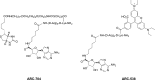
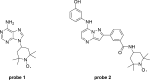
Protein kinases are important mediators of cellular communication and attractive drug targets for many diseases. Although success has been achieved with developing ATP-competitive kinase inhibitors, the disadvantages of ATP-competitive inhibitors have led to increased interest in targeting sites outside of the ATP binding pocket. Kinase inhibitors with substrate-competitive, ATP-noncompetitive binding modes are promising due to the possibility of increased selectivity and better agreement between biochemical and in vitro potency. However, the difficulty of identifying these types of inhibitors has resulted in significantly fewer small molecule substrate phosphorylation site inhibitors being reported compared to ATP-competitive inhibitors. This review surveys reported substrate phosphorylation site inhibitors and methods that can be applied to the discovery of such inhibitors, including a discussion of the challenges inherent to these screening methods.
Figures
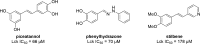


Similar articles
-
Quantitative proteomics of kinase inhibitor targets and mechanisms.ACS Chem Biol. 2015 Jan 16;10(1):201-12. doi: 10.1021/cb5008794. Epub 2014 Dec 17. ACS Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25474541 Review.
-
Discovery and Design of Novel Small Molecule GSK-3 Inhibitors Targeting the Substrate Binding Site.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 18;21(22):8709. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228709. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33218072 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in designing substrate-competitive protein kinase inhibitors.Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(20):2875-82. doi: 10.2174/138161212800672697. Curr Pharm Des. 2012. PMID: 22571656 Review.
-
Fluorescence labels in kinases: a high-throughput kinase binding assay for the identification of DFG-out binding ligands.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;800:95-117. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-349-3_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 21964785
-
Discovery and characterization of non-ATP site inhibitors of the mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinases.ACS Chem Biol. 2011 Mar 18;6(3):234-44. doi: 10.1021/cb1002619. Epub 2011 Jan 20. ACS Chem Biol. 2011. PMID: 21090814
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in the Development and Application of Radiolabeled Kinase Inhibitors for PET Imaging.Molecules. 2015 Dec 9;20(12):22000-27. doi: 10.3390/molecules201219816. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26690113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-based inhibitory peptide design targeting peptide-substrate binding site in EGFR tyrosine kinase.PLoS One. 2019 May 22;14(5):e0217031. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217031. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31116768 Free PMC article.
-
Application of a Substrate-Mediated Selection with c-Src Tyrosine Kinase to a DNA-Encoded Chemical Library.Molecules. 2019 Jul 30;24(15):2764. doi: 10.3390/molecules24152764. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31366048 Free PMC article.
-
ATP-competitive inhibitors for cancer treatment - kinases and the world beyond.RSC Med Chem. 2025 Jun 25. doi: 10.1039/d5md00235d. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40612269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UHMK1 promotes lung adenocarcinoma oncogenesis by regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Thorac Cancer. 2023 Apr;14(12):1077-1088. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14850. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Thorac Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36919755 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manning G.; Whyte D. B.; Martinez R.; Hunter T.; Sudarsanam S. (2002) The Protein Kinase Complement of the Human Genome. Science 298, 1912–1934. - PubMed
-
- Johnson S. A.; Hunter T. (2005) Kinomics: methods for deciphering the kinome. Nat. Methods 2, 17–25. - PubMed
-
- Ryšlavá H.; Doubnerová V.; Kavan D.; Vaněk O. (2013) Effect of posttranslational modifications on enzyme function and assembly. J. Proteomics 92, 80–109. - PubMed
-
- Pawson T.; Scott J. D. (2005) Protein phosphorylation in signaling – 50 years and counting. Trends Biochem. Sci. 30, 286–290. - PubMed
-
- Graves J. D.; Krebs E. G. (1999) Protein Phosphorylation and Signal Transduction. Pharmacol. Ther. 82, 111–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

