Launching a virtual decision lab: development and field-testing of a web-based patient decision support research platform
- PMID: 25495552
- PMCID: PMC4275953
- DOI: 10.1186/s12911-014-0112-8
Launching a virtual decision lab: development and field-testing of a web-based patient decision support research platform
Abstract
Background: Over 100 trials show that patient decision aids effectively improve patients' information comprehension and values-based decision making. However, gaps remain in our understanding of several fundamental and applied questions, particularly related to the design of interactive, personalized decision aids. This paper describes an interdisciplinary development process for, and early field testing of, a web-based patient decision support research platform, or virtual decision lab, to address these questions.
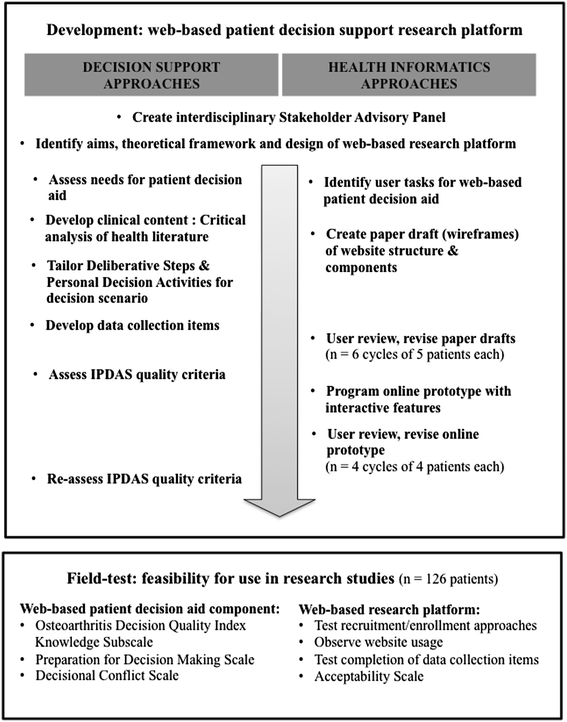
Methods: An interdisciplinary stakeholder panel designed the web-based research platform with three components: a) an introduction to shared decision making, b) a web-based patient decision aid, and c) interactive data collection items. Iterative focus groups provided feedback on paper drafts and online prototypes. A field test assessed a) feasibility for using the research platform, in terms of recruitment, usage, and acceptability; and b) feasibility of using the web-based decision aid component, compared to performance of a videobooklet decision aid in clinical care.
Results: This interdisciplinary, theory-based, patient-centered design approach produced a prototype for field-testing in six months. Participants (n = 126) reported that: the decision aid component was easy to use (98%), information was clear (90%), the length was appropriate (100%), it was appropriately detailed (90%), and it held their interest (97%). They spent a mean of 36 minutes using the decision aid and 100% preferred using their home/library computer. Participants scored a mean of 75% correct on the Decision Quality, Knowledge Subscale, and 74 out of 100 on the Preparation for Decision Making Scale. Completing the web-based decision aid reduced mean Decisional Conflict scores from 31.1 to 19.5 (p < 0.01).
Conclusions: Combining decision science and health informatics approaches facilitated rapid development of a web-based patient decision support research platform that was feasible for use in research studies in terms of recruitment, acceptability, and usage. Within this platform, the web-based decision aid component performed comparably with the videobooklet decision aid used in clinical practice. Future studies may use this interactive research platform to study patients' decision making processes in real-time, explore interdisciplinary approaches to designing web-based decision aids, and test strategies for tailoring decision support to meet patients' needs and preferences.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development and Field Testing of a Long-Term Care Decision Aid Website for Older Adults: Engaging Patients and Caregivers in User-Centered Design.Gerontologist. 2020 Jul 15;60(5):935-946. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnz141. Gerontologist. 2020. PMID: 31773140 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Effectiveness of a Web-Based Patient Decision Aid for Therapeutic Options for Sickle Cell Disease: Randomized Controlled Trial.J Med Internet Res. 2019 Dec 4;21(12):e14462. doi: 10.2196/14462. J Med Internet Res. 2019. PMID: 31799940 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Perceived barriers and facilitators of using a Web-based interactive decision aid for colorectal cancer screening in community practice settings: findings from focus groups with primary care clinicians and medical office staff.J Med Internet Res. 2013 Dec 18;15(12):e286. doi: 10.2196/jmir.2914. J Med Internet Res. 2013. PMID: 24351420 Free PMC article.
-
Web-Based Versus Usual Care and Other Formats of Decision Aids to Support Prostate Cancer Screening Decisions: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2018 Jun 26;20(6):e228. doi: 10.2196/jmir.9070. J Med Internet Res. 2018. PMID: 29945857 Free PMC article.
-
Developing an Internet-Based Decision Aid for Women Choosing Between Vaginal Birth After Cesarean and Planned Repeat Cesarean.J Midwifery Womens Health. 2015 Jul-Aug;60(4):390-400. doi: 10.1111/jmwh.12298. Epub 2015 Jun 8. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2015. PMID: 26059075 Review.
Cited by
-
What Rankings, Ratings, and Utilities Do Breast Cancer Patients Place on Tissue- and Implant-based Breast Reconstruction?Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2025 May 1;13(5):e6749. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000006749. eCollection 2025 May. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2025. PMID: 40321334 Free PMC article.
-
Introducing Decision Aids into Routine Prostate Cancer Care in The Netherlands: Implementation and Patient Evaluations from the Multi-regional JIPPA Initiative.J Cancer Educ. 2020 Dec;35(6):1141-1148. doi: 10.1007/s13187-019-01572-9. J Cancer Educ. 2020. PMID: 31278659 Free PMC article.
-
Decision Making When Cancer Becomes Chronic: Needs Assessment for a Web-Based Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Patient Decision Aid.JMIR Form Res. 2021 Jul 16;5(7):e27484. doi: 10.2196/27484. JMIR Form Res. 2021. PMID: 34269691 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress and implications of the application of large language model in shared decision-making in China's healthcare field.Front Public Health. 2025 Jul 10;13:1605212. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1605212. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40709042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electronically Verified Use of Internet-Based, Multimedia Decision Aids by Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes and Their Caregivers.MDM Policy Pract. 2018 Apr 18;3(1):2381468318769857. doi: 10.1177/2381468318769857. eCollection 2018 Jan-Jun. MDM Policy Pract. 2018. PMID: 30288443 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stacey D, Legare F, Col NF, Bennett CL, Barry MJ, Eden KB, Holmes-Rovner M, Llewellyn-Thomas H, Lyddiatt A, Thomson R, Trevana L, Wu JHC. Decision aids for people facing health treatment or screening decisions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;1:ᅟ. - PubMed
-
- Llewellyn-Thomas H. The Decision Research ‘lab’. In: Edwards A, Elwyn G, editors. Shared Decision-Making in Health Care. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2009. pp. 243–247.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous