Inhaled PGE1 in neonates with hypoxemic respiratory failure: two pilot feasibility randomized clinical trials
- PMID: 25496504
- PMCID: PMC4414424
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-15-486
Inhaled PGE1 in neonates with hypoxemic respiratory failure: two pilot feasibility randomized clinical trials
Abstract
Background: Inhaled nitric oxide (INO), a selective pulmonary vasodilator, has revolutionized the treatment of neonatal hypoxemic respiratory failure (NHRF). However, there is lack of sustained improvement in 30 to 46% of infants. Aerosolized prostaglandins I2 (PGI2) and E1 (PGE1) have been reported to be effective selective pulmonary vasodilators. The objective of this study was to evaluate the feasibility of a randomized controlled trial (RCT) of inhaled PGE1 (IPGE1) in NHRF.
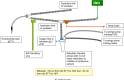
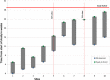
Methods: Two pilot multicenter phase II RCTs are included in this report. In the first pilot, late preterm and term neonates with NHRF, who had an oxygenation index (OI) of ≥15 and <25 on two arterial blood gases and had not previously received INO, were randomly assigned to receive two doses of IPGE1 (300 and 150 ng/kg/min) or placebo. The primary outcome was the enrollment of 50 infants in six to nine months at 10 sites. The first pilot was halted after four months for failure to enroll a single infant. The most common cause for non-enrollment was prior initiation of INO. In a re-designed second pilot, co-administration of IPGE1 and INO was permitted. Infants with suboptimal response to INO received either aerosolized saline or IPGE1 at a low (150 ng/kg/min) or high dose (300 ng/kg/min) for a maximum duration of 72 hours. The primary outcome was the recruitment of an adequate number of patients (n = 50) in a nine-month-period, with fewer than 20% protocol violations.
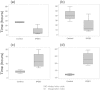
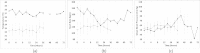
Results: No infants were enrolled in the first pilot. Seven patients were enrolled in the second pilot; three in the control, two in the low-dose IPGE1, and two in the high-dose IPGE1 groups. The study was halted for recruitment futility after approximately six months as enrollment targets were not met. No serious adverse events, one minor protocol deviation and one pharmacy protocol violation were reported.
Conclusions: These two pilot RCTs failed to recruit adequate eligible newborns with NHRF. Complex management RCTs of novel therapies for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN) may require novel study designs and a longer period of time from study approval to commencement of enrollment.
Trial registration: CLINICALTRIALS.GOV: Pilot one: NCT number: 00598429 registered on 10 January 2008. Last updated: 3 February 2011. Pilot two: NCT number: 01467076 17 October 2011. Last updated: 13 February 2013.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00598429 NCT01467076.
Figures

References
-
- Roberts JD, Jr, Fineman JR, Morin FC, III, Shaul PW, Rimar S, Schreiber MD, Polin RA, Zwass MS, Zayek MM, Gross I, Heymann MA, Zapol WM. Inhaled nitric oxide and persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn: the inhaled nitric oxide study group. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:605–610. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199702273360902. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Clark RH, Kueser TJ, Walker MW, Southgate WM, Huckaby JL, Perez JA, Roy BJ, Keszler M, Kinsella JP. Low-dose nitric oxide therapy for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn: clinical inhaled nitric oxide research group. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:469–474. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200002173420704. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Krieg P, Wahlers T, Giess W, Rohde R, Hartrumpf M, Bund M, Haverich A. Inhaled nitric oxide and inhaled prostaglandin E1: effect on left ventricular contractility when used for treatment of experimental pulmonary hypertension. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 1998;14:494–502. doi: 10.1016/S1010-7940(98)00210-3. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR442/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021385/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD34216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR41/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD068270/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD68263/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD068270/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21385/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR24128/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40689/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HD041423/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR93/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR59/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5K23HD041423/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD68278/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR70/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD36790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053109/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD053089/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR633/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD53109/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD53089/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024128/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040689/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD068263/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD068278/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD68270/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR32/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD036790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053089/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR42/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

