Will Fluoroscopic Follow-up after Stent-Assisted Coiling of Cerebral Aneurysms Provide Information on Recanalization?
- PMID: 25496679
- PMCID: PMC4295241
- DOI: 10.15274/INR-2014-10062
Will Fluoroscopic Follow-up after Stent-Assisted Coiling of Cerebral Aneurysms Provide Information on Recanalization?
Abstract
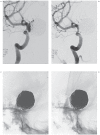
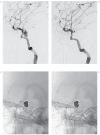
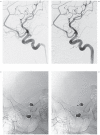
Fluoroscopic images for comparison (FICs) can be easily obtained for follow-up on an outpatient basis. This study retrospectively assessed the diagnostic performance of a set of FICs for evaluation of recanalization after stent-assisted coiling, with digital subtraction angiography (DSA) as the reference standard. A total of 124 patients harboring 144 stent-assisted coiled aneurysms were included. At least one month postembolization they underwent follow-up angiograms comprising a routine frontal and lateral DSA and a working-angle DSA. For analysis, FICs should be compared with the mask images of postprocedural DSAs to find recanalization. Instead of FIC acquisition, the mask images of follow-up DSAs were taken as a substitute because of the same view-making processes as FICs, full availability, and perfect coincidence with follow-up DSAs. Two independent readers evaluated a set of 169 FICs and DSA images for the presence of recanalization one month apart. Sensitivity, specificity, and interreader agreement were determined. Recanalization occurred in 24 (14.2%) cases. Of these, nine (5.3%) cases were found to have significant recanalization in need of retreatment. Sensitivity and specificity rates were 79.2% (19 of 24) and 95.9% (139 of 145) respectively for reader 1, and 66.7% (16 of 24) and 97.9% (142 of 145) for reader 2. Minimal recanalization was identified in seven out of all eight false negative cases. Excluding minimally recanalized cases in no need for retreatment from the recanalization group, calculation resulted in high sensitivity and specificity of over 94% for both readers. Interreader agreement between the two readers was excellent (96.4%; κ = 0.84). FICs may be a good imaging modality to detect significant recanalization of stent-assisted coiled aneurysms.
Keywords: embolization; fluoroscopy; follow-up studies; intracranial aneurysm; intracranial stent.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Reliability of dual- vs single-volume reconstruction of three-dimensional digital subtraction angiography for follow-up evaluation of endovascularly treated intracranial aneurysms.Interv Neuroradiol. 2016 Dec;22(6):687-692. doi: 10.1177/1591019916663469. Epub 2016 Aug 16. Interv Neuroradiol. 2016. PMID: 27530137 Free PMC article.
-
Contrast-Enhanced and Time-of-Flight MR Angiographic Assessment of Endovascular Coiled Intracranial Aneurysms at 1.5 T.Interv Neuroradiol. 2014 Dec;20(6):686-92. doi: 10.15274/INR-2014-10064. Epub 2014 Dec 5. Interv Neuroradiol. 2014. PMID: 25496678 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and efficacy of endovascular treatment of basilar tip aneurysms by coiling with and without stent assistance: a review of 235 cases.Neurosurgery. 2012 Oct;71(4):785-94. doi: 10.1227/NEU.0b013e318265a416. Neurosurgery. 2012. PMID: 22743359
-
Time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography for follow-up of coil embolization with enterprise stent for intracranial aneurysm: usefulness of source images.Korean J Radiol. 2014 Jan-Feb;15(1):161-8. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.161. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Korean J Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24497808 Free PMC article.
-
Kissing-Y stenting for endovascular treatment of complex wide necked bifurcation aneurysms using Acandis Acclino stents: results and literature review.J Neurointerv Surg. 2016 Apr;8(4):386-95. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2015-011691. Epub 2015 May 18. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016. PMID: 25987589 Review.
References
-
- Kwon BJ, Seo DH, Ha YS, et al. Endovascular treatment of wide-necked cerebral aneurysms with an acute angle branch incorporated into the sac: novel methods of branch access in 8 aneurysms. Neurointervention. 2012;7(2):93–101. doi: 10.5469/neuroint.2012.7.2.93. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kim BM, Park SI, Kim DJ, et al. Endovascular coil embolization of aneurysms with a branch incorporated into the sac. Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31(1):145–151. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A1785. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moret JC, Weill A. The "remodelling technique" in the treatment of wide neck intracranial aneurysms. angiographic results and clinical follow-up in 56 cases. Interv Neuroradiol. 1997;3(1):21–35. - PubMed
-
- Pierot L, Cognard C, Spelle L, et al. Safety and efficacy of balloon remodeling technique during endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms: critical review of the literature. Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33(1):12–15. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2403. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

