Treatment of complex intracranial aneurysms using flow-diverting silk® stents. An analysis of 32 consecutive patients
- PMID: 25496683
- PMCID: PMC4295245
- DOI: 10.15274/INR-2014-10070
Treatment of complex intracranial aneurysms using flow-diverting silk® stents. An analysis of 32 consecutive patients
Abstract
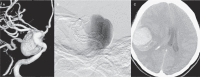
This study describes the peri-procedural and late complications and angiographic follow-up results of 32 patients with 34 complex aneurysms treated with flow diverter Silk stents in a single centre. In this retrospective study, 40 Silk stents (SS) were implanted in 34 complex intracranial aneurysms in 32 patients. In our series, 20 (58.8%) carotid-ophthalmic internal carotid artery (ICA), six (17.6%) cavernous ICA, two (5.9%) supraclinoid ICA, two (5.9%) petrosal ICA (the same patient- bilateral) and four (11.8%) posterior circulation aneurysms were treated. One of the posterior circulation lesions was a fenestrated-type aneurysm. Twenty wide-necked, saccular; eight neck remnant; four fusiform and two blister-like aneurysms were included in our series. SS were successfully implanted in all patients (100%). Misdeployment occurred in 17.6% of patients. In two of these patients adequate stent openness was achieved via Hyperglide balloon dilatation. Coil embolization in addition to SS placement was utilized in four aneurysms. One patient (3%) experienced transient morbidity due to a thromboembolic event and there was one mortality (3%) due to remote intraparenchymal haemorrhage. Complete occlusion of 27/33 (81.8 %) and 29/33 (87.9 %) aneurysms was achieved six and 12 months after the procedure, respectively. In-stent intimal hyperplasia was detected in 6.1 % patients. Flow-diverter Silk stent implantation is an effective method of treating complex aneurysms with acceptable mortality and morbidity rates. Complete occlusion is achieved in most of the complex aneurysms.
Keywords: Silk stent; cerebral aneurysms; endovascular treatment; flow diverter.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neurovascular reconstruction with flow diverter stents for the treatment of 87 intracranial aneurysms: Clinical results.Interv Neuroradiol. 2015 Jun;21(3):292-9. doi: 10.1177/1591019915582153. Epub 2015 May 11. Interv Neuroradiol. 2015. PMID: 25964435 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term occlusion results with SILK flow diversion in 28 aneurysms: Do recanalizations occur during follow-up?Interv Neuroradiol. 2015 Jun;21(3):300-10. doi: 10.1177/1591019915583119. Epub 2015 May 26. Interv Neuroradiol. 2015. PMID: 26015522 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of intracranial aneurysms by flow diverter devices: long-term results from a single center.Eur J Radiol. 2014 Sep;83(9):1683-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2014.05.029. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Eur J Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24985339
-
A rare but morbid neurosurgical target: petrous aneurysms and their endovascular management in the stent/flow diverter era.J Neurointerv Surg. 2017 Apr;9(4):381-383. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2016-012668. Epub 2016 Sep 26. J Neurointerv Surg. 2017. PMID: 27672098 Review.
-
Endovascular treatment of complex intracranial aneurysms by pipeline flow-diverter embolization device: a single-center experience.Neurol Res. 2015 Apr;37(4):359-65. doi: 10.1179/1743132814Y.0000000450. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Neurol Res. 2015. PMID: 25310354 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative analysis of characteristics, management, and clinical outcome of blood blister-like aneurysms treated with flow diverter devices: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 30 studies.Int J Surg. 2025 Jan 1;111(1):1427-1439. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002072. Int J Surg. 2025. PMID: 39288022 Free PMC article.
-
Clipping on Crossed Wrapping Method for Ruptured Blood Blister-Like Aneurysm of the Internal Carotid Artery: Technical Note and Long-Term Results.World Neurosurg X. 2019 Jan 4;2:100005. doi: 10.1016/j.wnsx.2018.100005. eCollection 2019 Apr. World Neurosurg X. 2019. PMID: 31218280 Free PMC article.
-
Coil embolization of pseudoaneurysm as a complication of excimer laser coronary angioplasty: insights from intravascular ultrasound and optical coherence tomography findings.J Med Ultrason (2001). 2019 Apr;46(2):245-249. doi: 10.1007/s10396-018-0908-8. Epub 2018 Oct 10. J Med Ultrason (2001). 2019. PMID: 30306440
-
Treatment of Intra- and Extracranial Aneurysms Using the Flow-Redirection Endoluminal Device: Multicenter Experience and Follow-Up Results.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017 Jan;38(1):105-112. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4964. Epub 2016 Nov 3. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017. PMID: 27811135 Free PMC article.
-
Silk® Flow Diverter Device for Intracranial Aneurysm Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Neurointervention. 2021 Nov;16(3):222-231. doi: 10.5469/neuroint.2021.00234. Epub 2021 Sep 14. Neurointervention. 2021. PMID: 34517469 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Molyneux AJ, Kerr RS, Yu LM, et al. International subarachnoid aneurysm trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised comparison of effects on survival, dependency, seizures, rebleeding, subgroups, and aneurysm occlusion. Lancet. 2005;366(9488):809–817. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67214-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shapiro M, Babb J, Becske T, et al. Safety and efficacy of adjunctive balloon remodeling during endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms: a literature review. Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29(9):1777–1781. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A1216. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lanzino G, Wakhloo AK, Fessler RD, et al. Efficacy and current limitations of intravascular stents for intracranial internal carotid, vertebral, and basilar artery aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 1999;91(4):538–546. doi: 10.3171/jns.1999.91.4.0538. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Velioglu M, Kizilkilic O, Selcuk H, et al. Early and midterm results of complex cerebral aneurysms treated with Silk stent. Neuroradiology. 2012;54(12):1355–1365. doi: 10.1007/s00234-012-1051-7. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

