Increased haemodynamic adrenergic load with isoflurane anaesthesia in type 2 diabetic and obese rats in vivo
- PMID: 25496763
- PMCID: PMC4266208
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-014-0161-4
Increased haemodynamic adrenergic load with isoflurane anaesthesia in type 2 diabetic and obese rats in vivo
Abstract
Background: Increasing numbers of type 2 diabetic and obese patients with enhanced rates of cardiovascular complications require surgical interventions, however they have a higher incidence of perioperative haemodynamic complications, which has been linked to adrenergic dysfunction. Therefore, we aimed to determine how α- and β-adrenoceptor (AR)-mediated haemodynamic responses are affected by isoflurane anaesthesia in experimental type 2 diabetes and obesity in vivo.
Methods: Sixteen-week old male Zucker type 2 Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) rats, Zucker Obese rats and their lean counterparts (n = 7-9 per group) were instrumented with radio telemeters to record blood pressure and heart rate and with vascular access ports for non-invasive intravenous drug delivery in vivo. Haemodynamic effects of α-AR (phenylephrine; 1-100 μg x kg(-1)) or β-AR (dobutamine; 2-120 μg x kg(-1)) stimulation were assessed under conscious and anaesthetised (isoflurane; 2%) conditions.
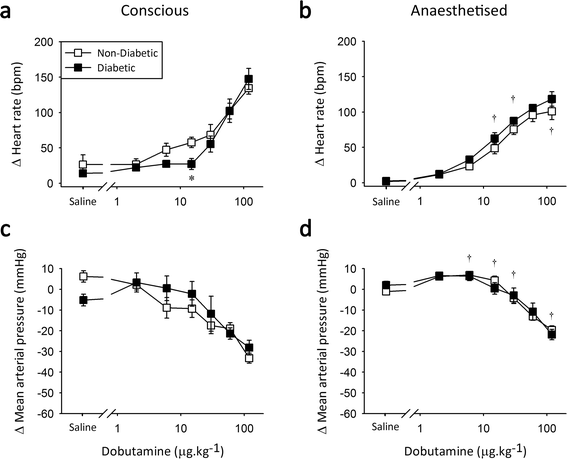
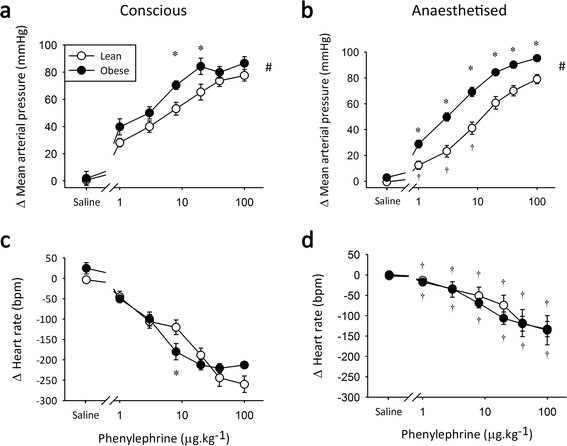
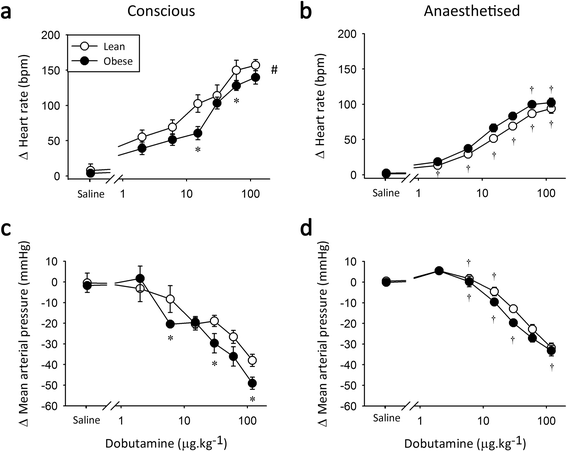
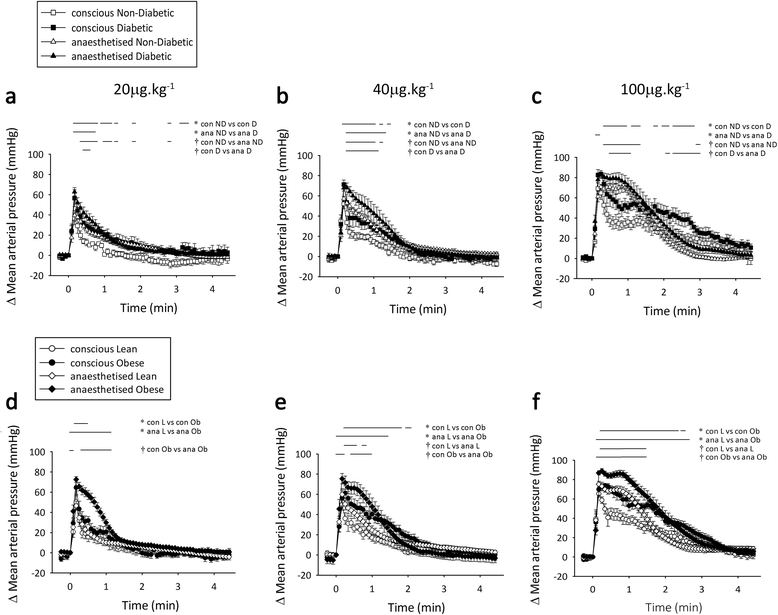
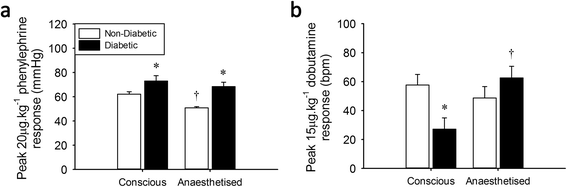
Results: Vascular α-AR sensitivity was increased in both diabetic (non-diabetic 80 ± 3 vs. diabetic 95 ± 4 ΔmmHg at 100 μg x kg(-1); p < 0.05) and obese (lean 65 ± 6 vs. obese 84 ± 6 ΔmmHg at 20 μg x kg(-1); p < 0.05) conscious rats. Interestingly, anaesthesia exacerbated and prolonged the increased α-AR function in both diabetic and obese animals (non-diabetic 51 ± 1 vs. diabetic 68 ± 4 ΔmmHg, lean 61 ± 5 vs. obese 84 ± 2 ΔmmHg at 20 μg x kg(-1); p < 0.05). Meanwhile, β-AR chronotropic sensitivity was reduced in conscious diabetic and obese rats (non-diabetic 58 ± 7 vs. diabetic 27 ± 8 Δbpm, lean 103 ± 12 vs. obese 61 ± 9 Δbpm at 15 μg x kg(-1); p < 0.05). Anaesthesia normalised chronotropic β-AR responses, via either a limited reduction in obese (lean 51 ± 3 vs. obese 66 ± 5 Δbpm; NS at 15 μg x kg(-1)) or increased responses in diabetic animals (non-diabetic 49 ± 8 vs. diabetic 63 ± 8 Δbpm, at 15 μg x kg(-1); NS at 15 μg x kg(-1)).
Conclusions: Long term metabolic stress, such as during type 2 diabetes and obesity, alters α- and β-AR function, its dynamics and the interaction with isoflurane anaesthesia. During anaesthesia, enhanced α-AR sensitivity and normalised β-AR function may impair cardiovascular function in experimental type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of type 2 diabetes, surgical incision, and volatile anesthesia on hemodynamics in the rat.Physiol Rep. 2017 Jul;5(14):e13352. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13352. Physiol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28716819 Free PMC article.
-
β1 -Adrenoceptor, but not β2 -adrenoceptor, subtype regulates heart rate in type 2 diabetic rats in vivo.Exp Physiol. 2017 Aug 1;102(8):911-923. doi: 10.1113/EP086293. Epub 2017 Jun 9. Exp Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28543947
-
Cardiac β-Adrenoceptor Expression Is Reduced in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats as Type-2 Diabetes Progresses.PLoS One. 2015 May 21;10(5):e0127581. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127581. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25996498 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms underlying electro-mechanical dysfunction in the Zucker diabetic fatty rat heart: a model of obesity and type 2 diabetes.Heart Fail Rev. 2020 Sep;25(5):873-886. doi: 10.1007/s10741-019-09872-4. Heart Fail Rev. 2020. PMID: 31654177 Review.
-
Fostering orphan receptors: an indispensable role for integrative, in vivo, haemodynamic studies.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2003 Apr;3(2):140-5. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4892(03)00004-3. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12681235 Review.
Cited by
-
Exogenous and endogenous angiotensin-II decrease renal cortical oxygen tension in conscious rats by limiting renal blood flow.J Physiol. 2016 Nov 1;594(21):6287-6300. doi: 10.1113/JP270731. Epub 2016 Aug 18. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27426098 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological treatment of type 2 diabetes in elderly patients with heart failure: randomized trials and beyond.Heart Fail Rev. 2023 May;28(3):667-681. doi: 10.1007/s10741-021-10182-x. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Heart Fail Rev. 2023. PMID: 34859336 Review.
-
Effect of type 2 diabetes, surgical incision, and volatile anesthesia on hemodynamics in the rat.Physiol Rep. 2017 Jul;5(14):e13352. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13352. Physiol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28716819 Free PMC article.
-
Epicardial adipose tissue: an emerging biomarker of cardiovascular complications in type 2 diabetes?Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2020 May 25;11:2042018820928824. doi: 10.1177/2042018820928824. eCollection 2020. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32518616 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory effects of anesthetics in obese patients.World J Crit Care Med. 2017 Aug 4;6(3):140-152. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v6.i3.140. eCollection 2017 Aug 4. World J Crit Care Med. 2017. PMID: 28828299 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

